http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/RB-MOVEMENT-3.pdf
WORKOUTS (BASIC)
Elite Football Combine Preparation – Movement
Elite football combine prep movement training can be a challenging periodization to plan for since there is a short mesocycle of typically 8 weeks. The goal is to reach the highest genetic potential of speed for each athlete safely but quickly. You will see how we periodize for our combine training down to the week, day, and exercise.
The format we use to lay out the periodization is organized so we can see the day and type of training to the left. Moving to the right you’ll see the aspect of training weather its CAMPS (CNS Activation and Muscle/Joint Preparation Systems), plyometrics, technical drills, or application drills. Our CAMPS are always first and designed to specifically prepare the athlete for the type of training planned for that day. For instance, Mondays and Thursdays are agility days that involve lots of lateral change of direction may dictate that more lateral lunging or hip adduction/abduction focused exercises will be implemented into CAMPS. Plyometrics typically follow CAMPS. Application typically follows the plyometrics and the technical drills are implemented between application drills based on flaws the athlete may present during the application drill. The volume (reps and sets) for each application drill depends on form and injury imitations. Typically, if the athlete is healthy high volume of basic level speed work is recommended in the first week. The focus of Tuesdays and Fridays is linear speed. Wednesday is our active recovery day with the focus on doing speed drills in our Olympic pool. The pool allows us to de-load the joints since the pool water will support half the weight of the athlete.
Week 1 is our general preparatory phase (GPP). In this phase the athletes are medically evaluated to identify imbalances. Our exercises are designed to balance the athlete then progressively overload the body to solidify the bilateral muscle balance. Much of emphasis is put building a base level of strength so the muscles can adapt to basic speed drills. The more high level advanced training is dependent on the base level GPP adaptation to speed training to maximize speed and avoid injury. There is a heavy emphasis on learning technique for agility and 40-yard dash starts. Lots of resistance speed training is utilized to work on the acceleration phase.
Week 2 is our intensification phase. More volume is added to the exercises introduced in the GPP phase. Also, longer buildups into the a-run exercises are added along with more heavy resistance training on acceleration sprint training. In this phase we will introduce phase 1 of assisted sprint training. The assistance will be really short with maybe just for the first step of a 10-yard sprint. This drill is high-risk high reward, which is why there is multiple phases the progress in intensity. Only athletes that are healthy will partake in assisted work.

Week 3 drills progress in volume, resistance, and distance of each drill. Phase 2 of overspeed is introduced with ankling and buttkick drills. The athletes’ muscles are now prepped for higher intensity drills such as phase 2 of over speed.
Week 4 focuses on longer a-run zones with faster build-up runs. Phase 3 of overspeed is now safe to implement. Distance of pulls and runs for overspeed is determined by form and/or medical limitations.

In the 5th week of training volume is slightly decreased with increased intensity being the goal. The amount of drills at this point is limited to 1-2 sets. This means the athletes should perform these sets and reps with aggressive speed and power while maintaining ideal form. Staying with the theme of increase intensity, the overspeed drills are a main goal for the linear days. This is the drill that will help guys get the extra speed needed to lower their 40-yard dash time. Agility drills are performed from start to finish without being practiced in its parts. It’s important that all weight room and muscle preparation exercises before speed work minimizes the hamstring specific drills if not completely avoided. We want the athlete to train hard in week 5 but keeping in mind week 6 is their first mock combine. For athletes invited to Indianapolis NFL combine, this mock will be their true mock combine.

Week 6 is mock combine week. All athletes going to the NFL combine will take this day seriously to closely as possible mimic their testing day at the NFL combine. These athletes will only be about 75-80% recovered at this point due to the week 5 training. Also, this day and the testing numbers that is yielded will just be an estimate for their potential. The athletes’ highest genetic potential should be peaked exactly on their proday or combine testing day, assuming the athletes have no injuries or experience any other unforeseen issues. We typically bring our athletes to the ocean the day after the mock combine-testing day to speed up recovery times. The rest of the week is designed to correct flaws in any of the drills that we videotaped for each athlete on the mock combine day. Also, hamstring exercises are avoided to allow them to recover faster.

Week 7 is one of our last high intensity moderate volume training weeks. By this time athletes are adapted to the stress of overspeed training and running full speed or more than full speed for 30-60 yards. We are confident that all healthy athletes can increase the intensity and volume of their overspeed runs by pulling harder and assisting the sprints for greater distances. Keep a good rest time of around 2-3 minutes between pulls to allow the muscles to recover. On day 1 athletes going to the NFL combine will only do the combine camps and full speed agility drills for about 1-2 sets each. On day 2, their last mock combine may be limited to a maximum distance of 20-yard sprints to ensure their muscles are not over trained. This last mock focuses on perfecting 40-yard dash starts and correcting any flaws from their previous mock combine. All athletes will end the week with full speed agility drills and a low volume linear speed day with possible low volume overspeed sprints.

The final week 8, most athletes are using day 1 to taper down for their true mock combine on day 2. NFL combine athletes are also still tapering down from the previous week since they fly out and travel to Indianapolis. The NFL combine guys do strictly combine camps and practice starts with strategic “off days.” Hydration is a key focus due to weather and surrounding changes that can dehydrate athletes. If the combine athlete follows our taper regimens and does not change the usual routine, he will peak and perform well on his assigned testing day. All other athletes in this final week will perform their day 2 true mock combine followed by a recovery day on day 3. For their final day 4 and 5, most of the athletes will begin their taper sheets and travel to their school and peak on their testing proday.

Eilite Football Combine Preparation – Strength
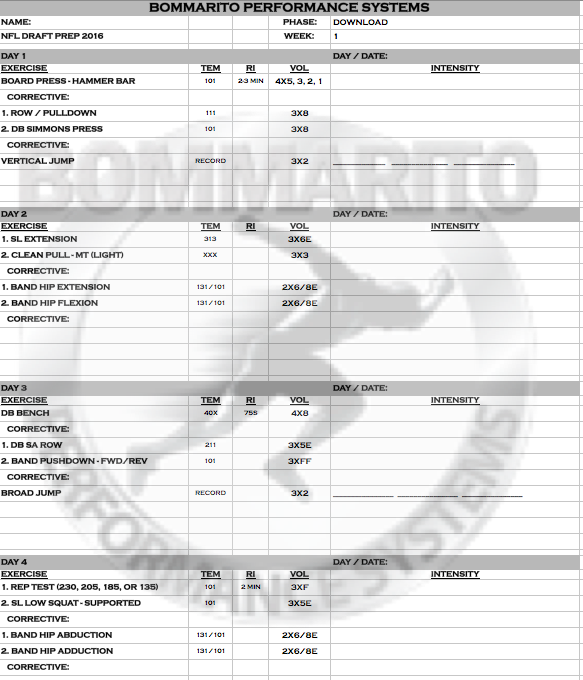
Most athletes, sooner or later, will need to prepare for various measures of athletic performance tests such as the 40 yard dash, 3-cone drill, 5-10-5 shuttle, vertical jump, and broad jump. As strength and conditioning specialist its important to have an appropriate, effective, and efficient deigned strength program that will enhance athletic performance. For example, training collegiate athlete transitioning from NCAA football into the NFL, requires athletes to perform at their highest genetic potential. Below are the first 4 weeks of the BPS Elite Football Combine Prep periodization.
First, is the General Preparatory Phase (GPP). This first week involves performing pre tests for 3 of the athletic performance tests (225 bench press, vertical jump, and broad jump). This helps to gauge any imbalances each athlete has so a tailored strength program can be utilized. Once this is complete the athlete begins the strength progressions. In this week, the goal is to quickly realign the body bilaterally through the use of single arm and single leg exercises, neural adaptation, and hypertrophy. Also, this phase involves adapting the muscle tissue with volume in preparation for more aggressive high speed power. 
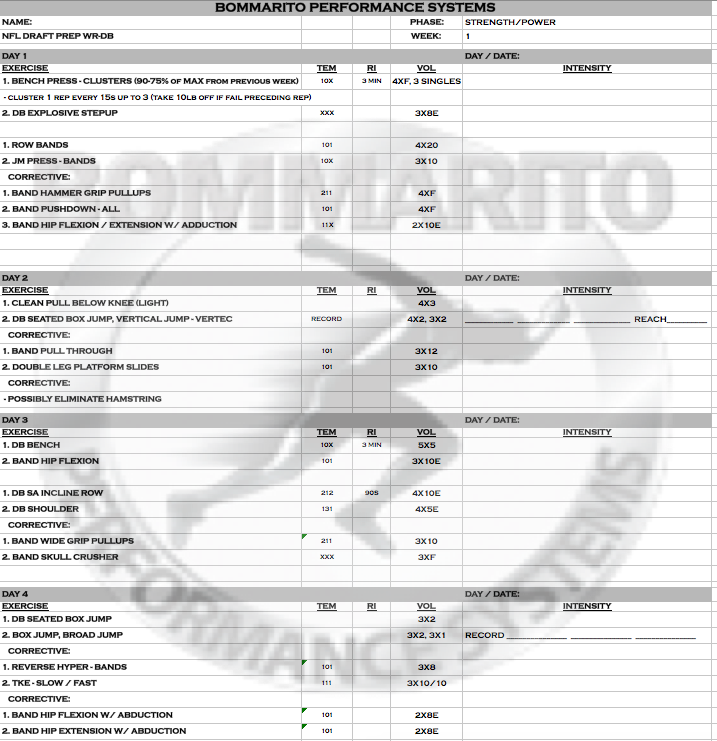
As we progress to the next week of strength training called the intensification phase, we put an emphasis on increasing the intensity of training, as the phase name describes. The concept of variable resistance is introduced to increase to further increase neural adaption by recruiting more motor units within the target muscles. More volume is added for increased hypertrophy and strength. Variable resistance such as bands and/or chains will increase strength for more of the muscles range of motion and as the bodies mechanical advantage increases.

In the third week of training, the athlete will move to the conjugate phase of strength training. The goal of this phase is to progress from hypertrophy and strength training into the power phase. This can be accomplished with more variable resistance along with faster tempos during the exercises. The first week of conjugate training is considered more strength than power training.
The concept of the Conjugate phase is to have one day of upper in the Strength and Max Strength levels; and the other day of upper in the Speed-Strength and Power Levels. The same concepts will follow for the lower body – one day SL Strength and Max Strength with the other day being Speed-Strength and Power. Note a lot of the Speed-Strength and Power is with the use of variable loading on multi-joint lifts of bench and squat, which emphasizes acceleration through the end range of motion.

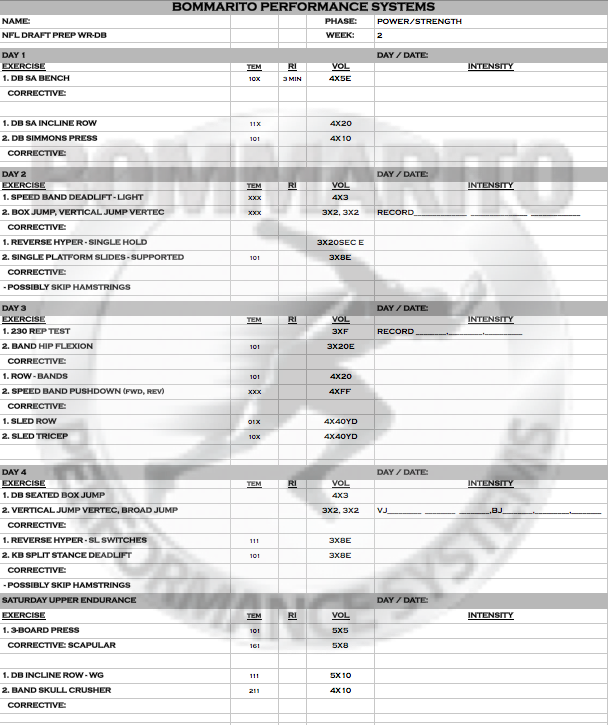
Progressing to the second phase of conjugate training overloads the strength and power built in phase 1 of conjugate. More volume is added and more variable loading is added.

After week 4 of draft prep training, most athletes will be due for a downloaded lift in the weightroom. With this basic download lift week, the focus is to bring the volume down for upper and lower body days. Depending on the athlete, downloading the lower body and uploading the upper body may be appropriate. During this time of the year athletes will be invited to play in collegiate bowl games. If an athlete attends this week-long game he will not lift for that week and therefore, that counts as his download week. The low volume and/or no lift, allows the body to actively recover from the previous weeks of conjugate dynamic. Upon completion of this week, the athlete will be ready to increase the strength plateau by advancing into the next strength/power and power/strength phases.

The strength/power phase focuses on a big increase in intensity with emphasis on strength slightly more than power development. The first upper body day 1, with “clusters,” increases pressing strength dramatically. Pulling and elbow extensor volume is increase for more upper body strength, power, and endurance. The lower body days are designed to potentiate power output. Many resisted jumps paired with free jumps are effective in this phase. This jumping power will also transfer to the sprint training, which is preparing the athletes to peak in a few weeks.

The following power/strength phase focuses more on power output than strength gains. The previous weeks have prepared the muscles for massive gains in hypertrophy and strength, leading the athlete to peak performance for maximum power. Upper body days emphasize pushing power and realizing new plateaus for the 225lb bench press rep test. The lower body resisted jumps and clean pulls are light to focus on potentiating power through faster movements. Then, realizing the new plateaus for the broad and vertical jumps.

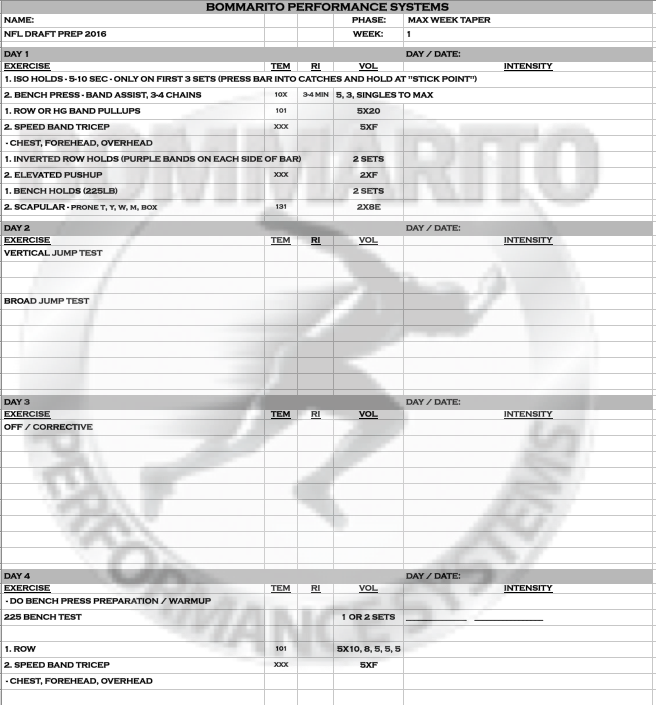
The final strength phase is the max/taper phase, which focuses on upper max strength through heavy weight with a power component by adding chains. Most of the pushing is fast and pulls are reflexive. The inverted row holds are designed to isometrically strengthen the muscles that are contracted at the bottom of the bench. This isometric strength will produce a more powerful stretch reflex on a 225lb bench press rep test. The 225lb bench holds are designed to isometrically strengthen the muscles involved in keeping the bench press body position base and elbow extensors that are keeping the arms straight. This strength will allow the athlete to have a temporary regrouping moment to make sure the body is properly positioned to perform single repetitions under fatigue during the end of an actual 225lb bench press test.

Professional Tennis Conjugate Strength

This conjugate strength week is designed for the professional tennis athlete who is injury free and 4-8 weeks into their offseason periodization. Remember, a tennis “pro” isn’t necessarily 18 years of age or older. Some “pro” tennis players can be as old as 14 years and have enough training experience to appropriately progress to this phase of strength training.
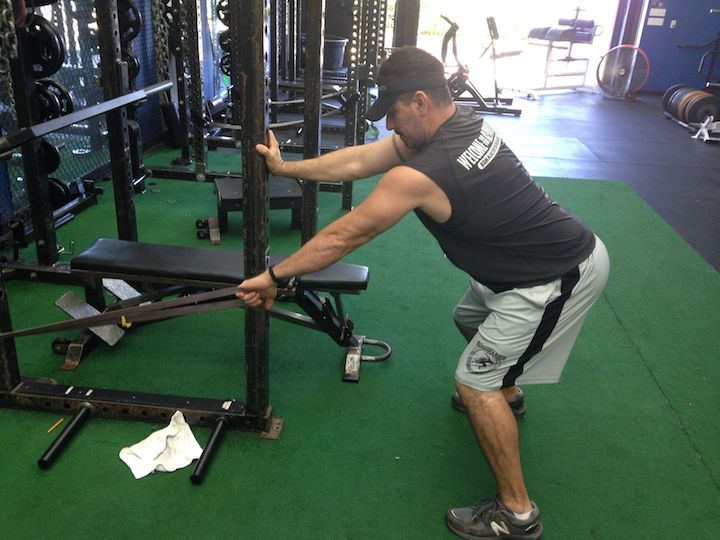
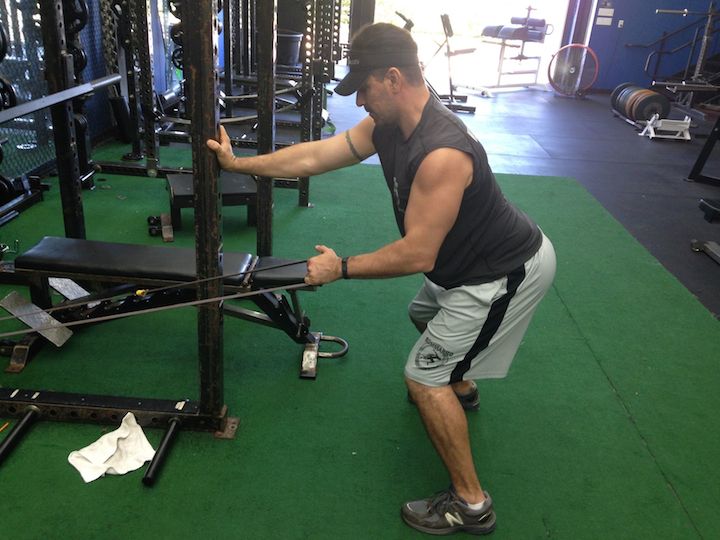
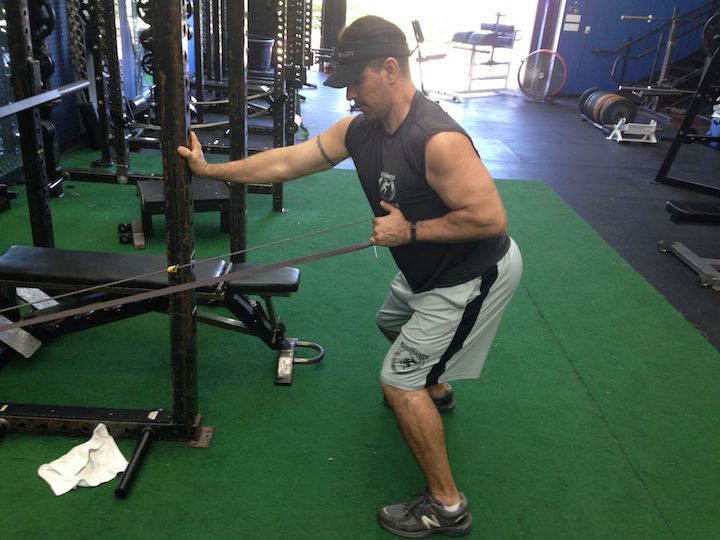
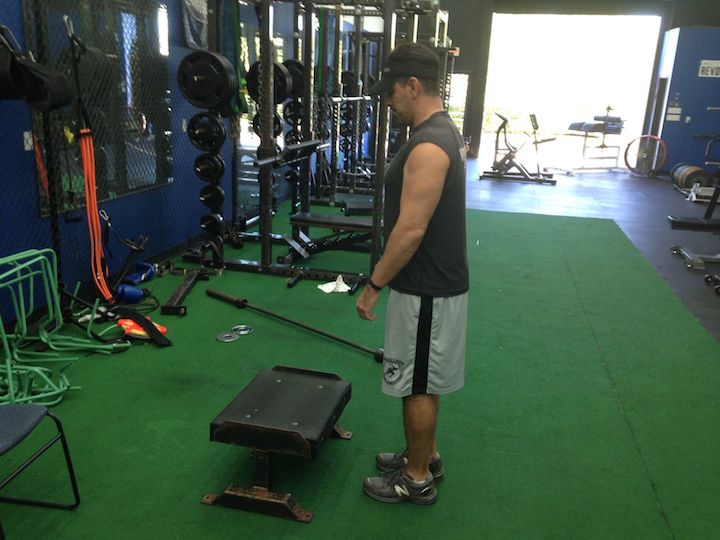
As referenced in some of our variable resistance article, it’s necessary to utilize bands or chains with lower body pressing motions to increase power output. This increase will translate to linear speed, lateral quickness and leaping abilities. For a video reference of each exercise refer to our database.
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Screen-Shot-2016-11-03-at-10.31.20-AM.pdf
Auxiliary Pain Management
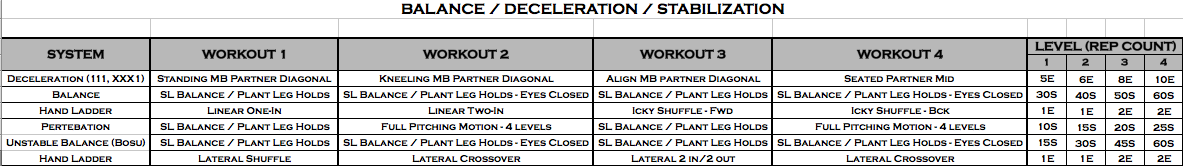
Foot/Ankle – Knee – Scapular Correctives
Below are some exercises that may be implemented into any program including rehabilitation, pain management, pre-habilitation, or general strengthening. The tempos, range of motion, and volume for each exercise depend on training experience and in some cases time out of surgery. For the video demonstrations, navigate to our exercise database!
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Screen-Shot-2016-11-02-at-4.39.03-PM1.pdf
Elite Soccer Inseason/Offseason
Here is and in-season and off-season movement workout which can be done with professional/elite soccer players. As always, start with CAMPS and progress into the work for the day.
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/ELITE-SOCCER-ESD.pdf
Football Running Back Specific Scripts
Football Running Back Specific Scripts
Below is an article written by NFLUP based on our BPS principles and athlete feedback. This reading is a preclude to the example running back specific weightroom and movement scripts scripts and will help you understand our concepts.
New York Giants running back Rashad Jennings is coming off a monster week, rushing for 176 yards in a 30-17 win over the Houston Texans in Week 3. Having a unique workout regimen, Jennings writes about how he prepares for game time.
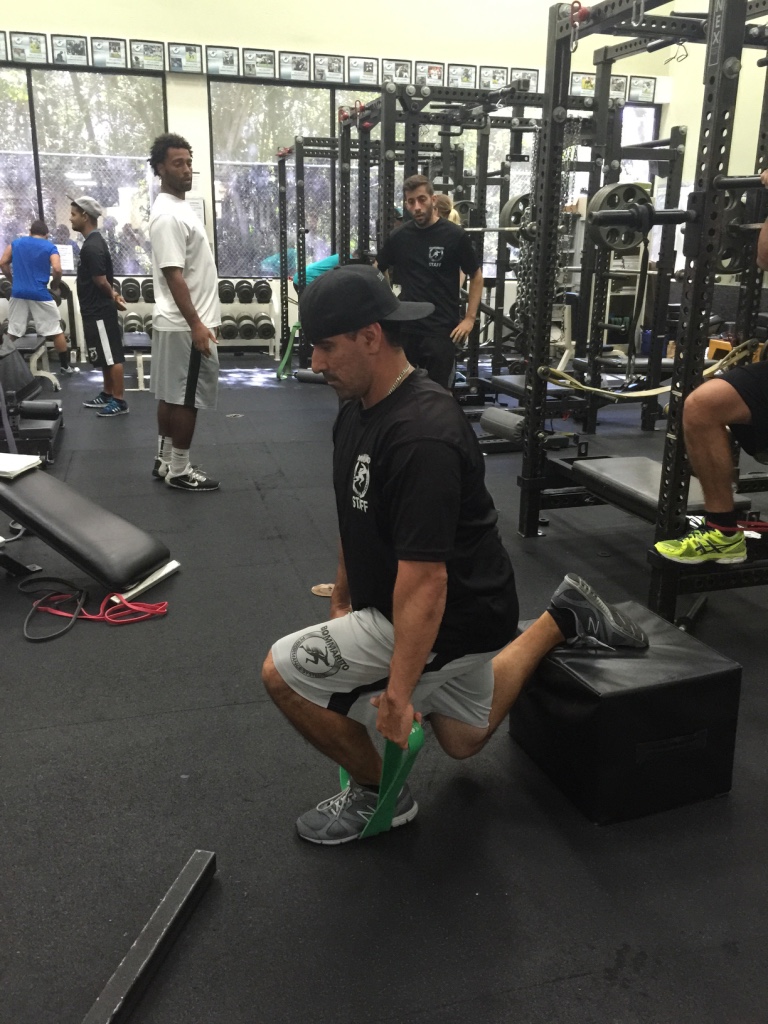
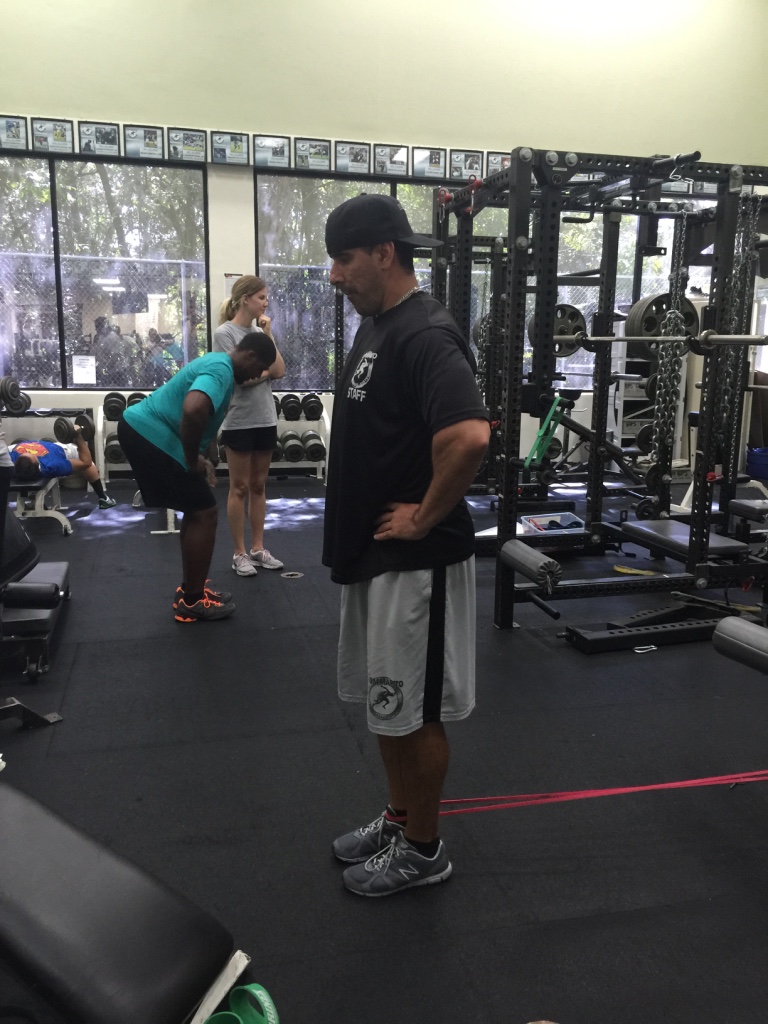
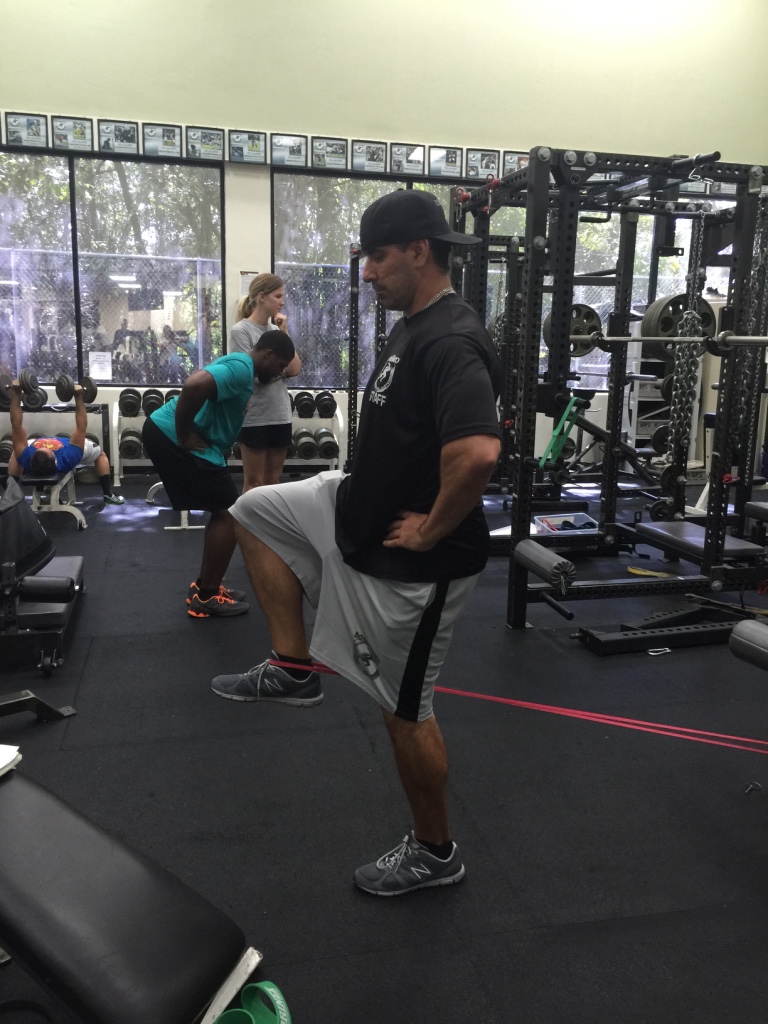
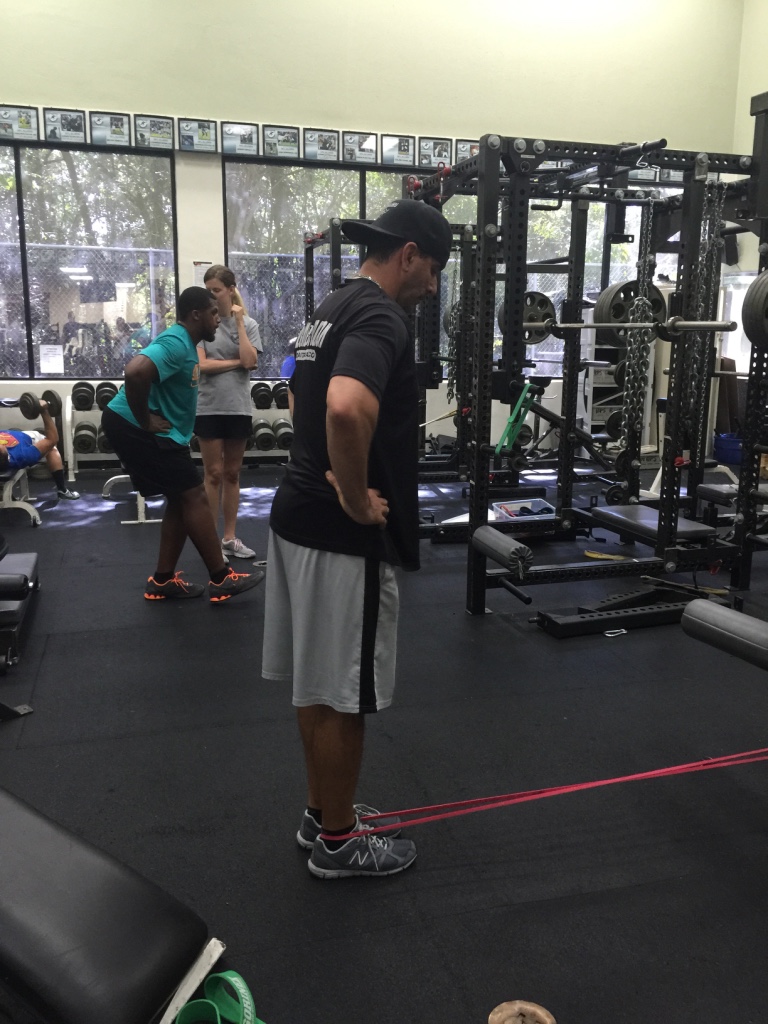
I start every speed/movement/conditioning workout with a preparation sequence specifically designed for the foot and ankle. As a running back, there is so much emphasis on quick decelerations and burst into re-acceleration, aggressive change-of-directions and the ability to cut off either edge of either foot at any angle.
The systematic sequence I use for preparing the foot and ankle joints includes:
1. Absorbing force
2. Accepting body weight
3. Redirecting the force
This sequence keeps the joints in my foot and ankle strong, stable and able to absorb and redirect high levels of force to safely and efficiently perform all of the movements required of a high-level running back.
I have a team of medical specialists that help to keep my body in the perfect aligned state. My medical team doesn’t just rehabilitate injuries or regenerate my body for the season; it ensures that my joints are aligned properly and my muscles are consistently at their maximum capabilities of contracting. A running back’s body takes a lot of abuse. This systematic approach of using over a dozen different medical disciplines over the course of the offseason keeps my workouts as efficient as possible, without adding any unnecessary stress to the joints.
New York Giants running back Rashad Jennings keeps his legs strong with these weighted squats. (NFL)
My workouts in the weight room incorporate everything. Too many times in training, people get stuck on doing only what they enjoy, or what they’re good at. To be a high-level athlete where speed, strength, power and agility are a premium, you need a constant dose of different types of training mechanisms.
I strive to intelligently incorporate everything, including:
» Free weights to maximize neural development
» Machines to isolate specific muscles, especially the “weak links” in my overall chain
» Power based exercises
» Maximum strength multi-joint lifts
» Variable loading to focus on accommodating resistance – both maximum strength and power-based exercises
» Trunk/spine exercises – strength, power and isometric based

Want to see more great tips from the NFL elite? Visit NFL Up! for videos and tips to get football fit. More…
I put a premium on linear speed. Many people talk about it not being “sport-specific.” Linear speed is general, but it gets my muscles prepared properly in all different phases: dynamic strength, endurance, power, high-speed eccentric loading, etc. Sometimes it’s necessary to train the muscles, not try and recreate the motions for a position or a sport. Training needs to be aggressive, but well thought out. Even though straight line and linear speed might not exactly apply to my motions on the football field, it definitely prepares my muscles properly to execute football moves.
When it is time to incorporate specific motions and movement patterns that are required at running back, it needs to be quick and to the point. No wasted motions and no wasted reps. The patterns I incorporate include:
» Jump cuts
» Quick jump cuts
» Inside edge cuts
» Outside edge cuts
» Planned cuts
» Unplanned cuts off of a visual/verbal stimulus
» Rounded multi-directional motions (specifically for passing routes)
» Deceleration/Re-acceleration
» Resisted work
» Assisted work
As a running back, I am dedicated to putting 110% into aggressive, intelligent physical preparation. When position-specific work is intelligently incorporated into my overall program, it produces tremendous benefits. This advanced form of training properly focuses with the right amount of volume and intensity. Timed appropriately throughout the offseason, this ensures that I’ll build up an adequate base of power, speed, endurance and agility to maximize my contributions on the field.
Jennings would like to thank everyone at Bommarito’s Performance Systems in Miami, who designed specialized programs that include the components described in this post. To see a full workload from the breakout back, check out his NFL Up! workout page.
Rashad Jennings is a 6-year veteran NFL running back currently playing for the New York Giants. He established the Rashad Jennings Foundation, which provides mentorship for individual success while promoting health and fitness worldwide.
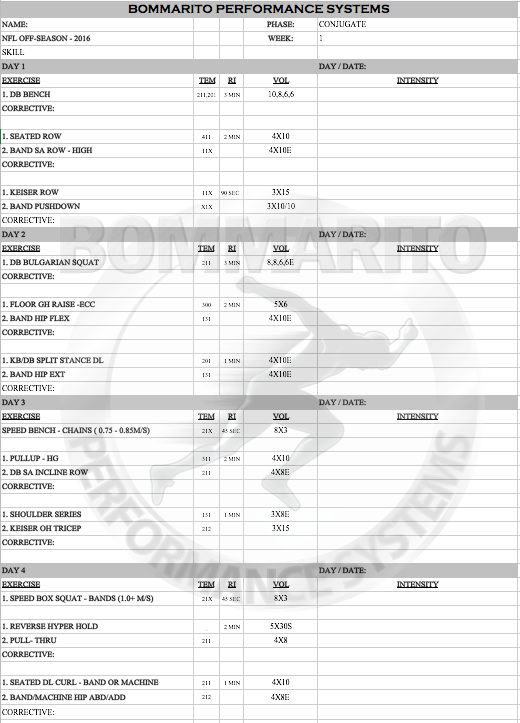
Football Running Back Specific Scripts
Weightroom:
Movement:
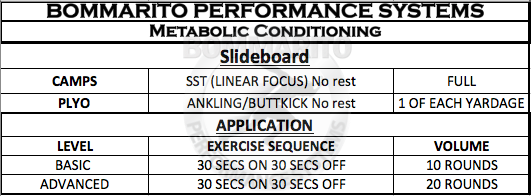
Metabolic Conditioning – Low Impact (Slideboard)
Slideboard
A typical metabolic conditioning method is running or sprinting for given times. This is a very effective method and one we use frequently. However, there are ways to challenge this system with low impact training. Therefore, we utilize the slideboard equipment. After a fast pace SST muscle prep with the ankling/buttkick plyos, use no rest time between exercises, transition 2 minutes later into the slideboard work. Make sure the slideboard is sprayed with the proper anti-stick formul and proper shoe booties. Have enough slideboards to allow athletes to abide by the rest time (1 person on 1 person off). Encourage the athlete to keep a fast pace while pushing side to side. Below is an example script we use for our professional athletes.
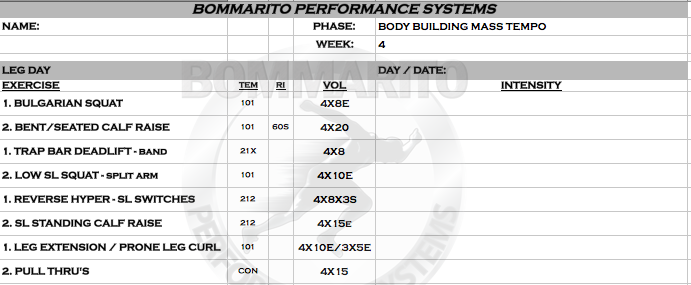
Grow Your Legs!
For those of you fitness enthusiast who want to increase leg girth, try this leg workout for a few weeks in your routines. Expect to see hypertrophy of the quads, calves, gluts, and ham’s. This workout can hypertrophy the legs without the use of putting a bar on your back or shoulder. If you’re someone who likes to avoid loading the spine, for instance a back squat, but still want to grow your legs then this workout is for you!
Workout Script:
Strength / Endurance Training On The Road
Strength/endurance on the road
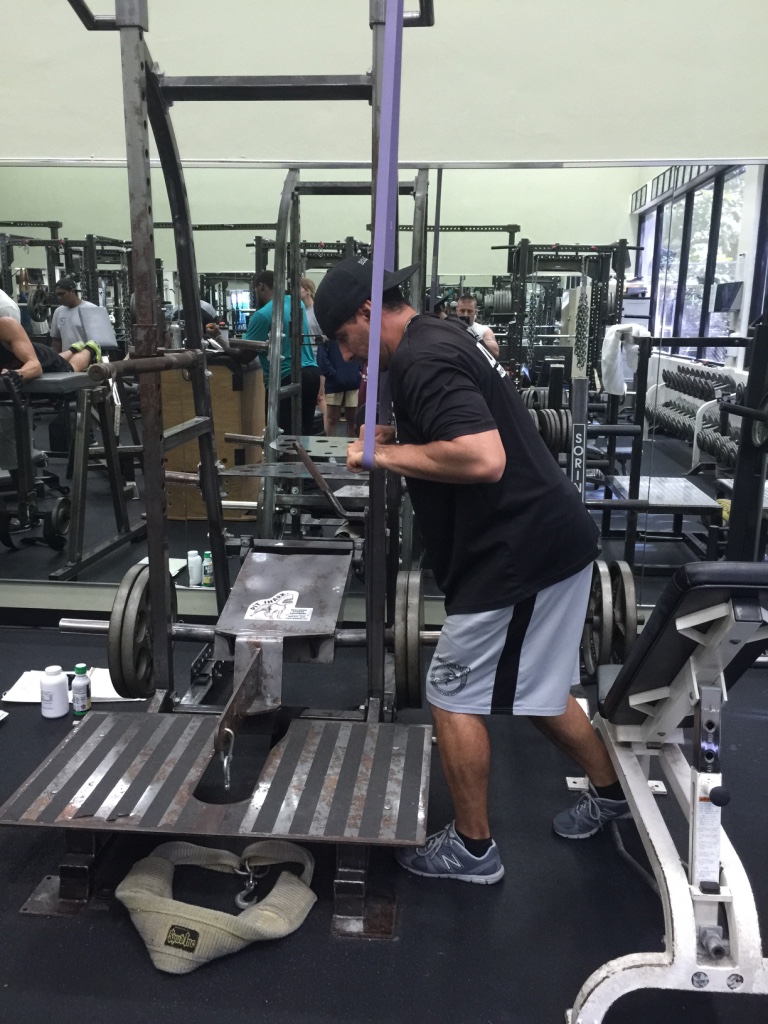
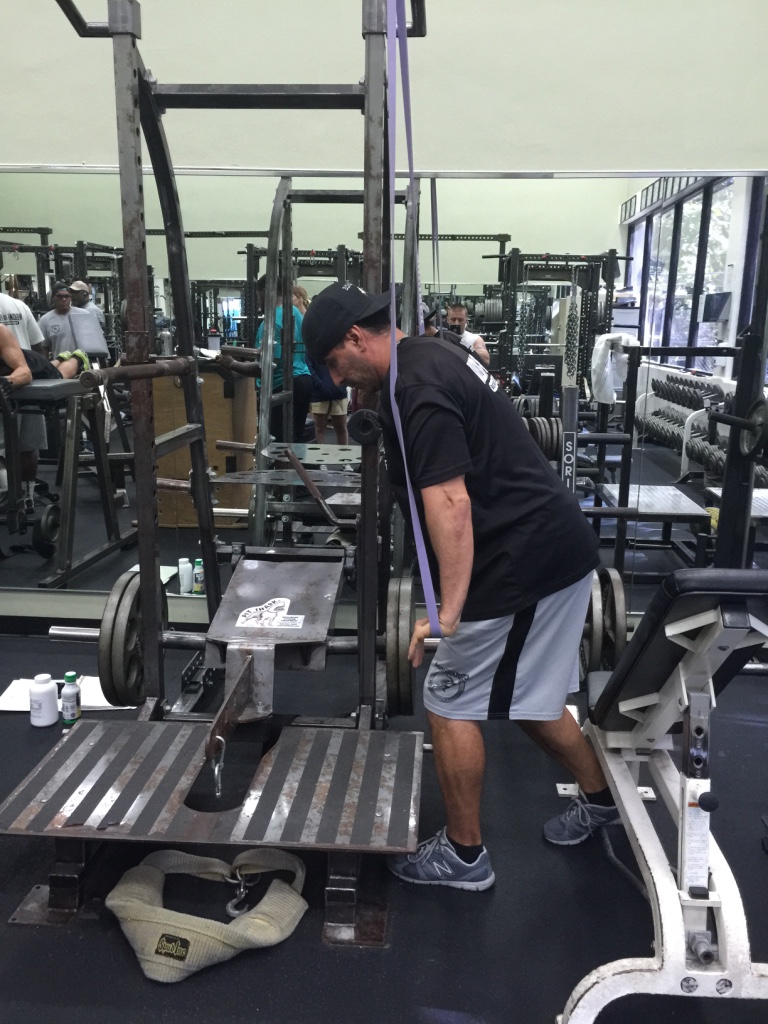
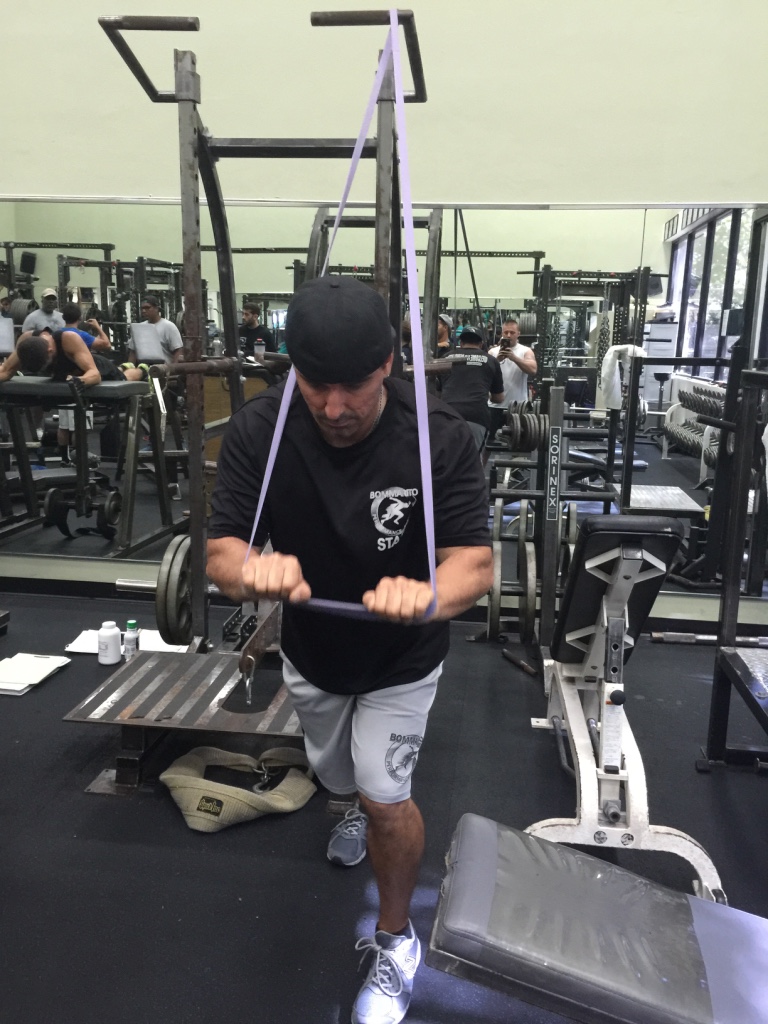
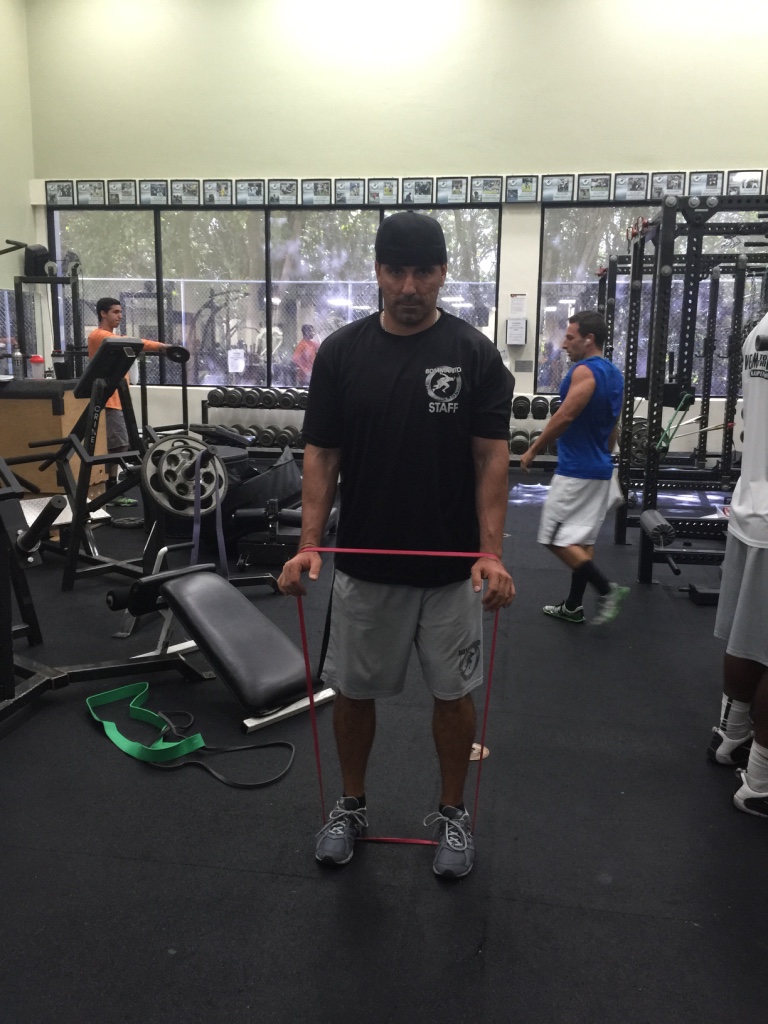
Many people have jobs that require them to travel. Sometimes the gyms they have access to are full scale and sometimes they don’t exist. This program solves such an issue. Sorinex bands are easy to travel with and cheap to buy. Other equipment necessary for this program are simple things most every gym would have such as a bench.
These exercises by nature will increase upper body and lower body strength. However, the variables such as the rest intervals, reps, tempos and sets will challenge the persons’ endurance. When advancing in resistance keep in mind you want to maintain the same variables of the exercise just as efficient as when the resistance was lighter.
Equipment needed:
Sorinex band assorted resistance and a bench
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Band-workout-on-the-road-high-volume.pdf
Soccer Field Strength Program
Soccer on the field strength training
Here is an example of a conjugate type program that can be done out on a filed or anywhere that is not in a weightroom. It’s important for soccer players to do strength training, although it is sometimes neglected due to the struggles of fitting a team inside a standard weightroom. The equipment necessary is minimal and listed below. This conjugate method will increase the strength and dynamic strength of soccer athletes to help avoid injury and improve sport performance.
The volume is moderate but the intensity is high. Stay discipline with the set tempos, rest intervals, sets and reps. As always, reference the listed exercises in the exercise database for a quick visual demonstration. For a more detailed demonstration reference the coaching videos.
QUIPMENT NEEDED:
Sorinex Bands – Mini, Monster-Mini, Light, Medium, Heavy
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Example-Soccer-Field-Strength-6-16-16.pdf
BASEBALL BASE-STEALING SCRIPT
German Volume Training – Complexes Week 1-2
German Volume Training – Complexes Week 1-2
This bodybuilding type of program should be completed for two consecutive weeks. This program puts into play building muscle (hypertrophy) through the principles of increased volume and increased time the muscle are under tension. It is important to stay true to the rest times and the mode of exercise for best results.
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/WORKOUT-BUILDER-German-Volume-Complexes1.pdf
German Volume Training (Complexes)
8-17-16
Adam Boily MS, MATJS, USAW
German Volume Training (Complexes)
Here are the main points to understand and keep in mind:
- The structure – Each day begins with a corrective exercise designed to supplement the theme for the day. For example, if the theme of the day is upper body, you may begin with rotator cuff work. Second, you’ll notice the numbers next to the exercises. If two exercises are to be paired, you’ll see a “1” and a “2.”
- Notice that each day works to build opposing muscles. The first two complexes are press focused while the second two complexes are pull focused. Complete all exercises starting at the top and reading down for each day.
- The main concept for building muscle with this style of workout is “time under tension.” This means the muscle will hypertrophy the more time it is placed under tension. We accomplish this with long tempos (i.e. 402), working 6 days a week as well as with high volume (i.e. 5×5). As the athlete becomes stronger/muscle grows, the more weight he or she can handle and the more the muscle will hypertrophy.
http://bpsuniversity.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/WORKOUT-BUILDER-German-Volume-Complexes.pdf
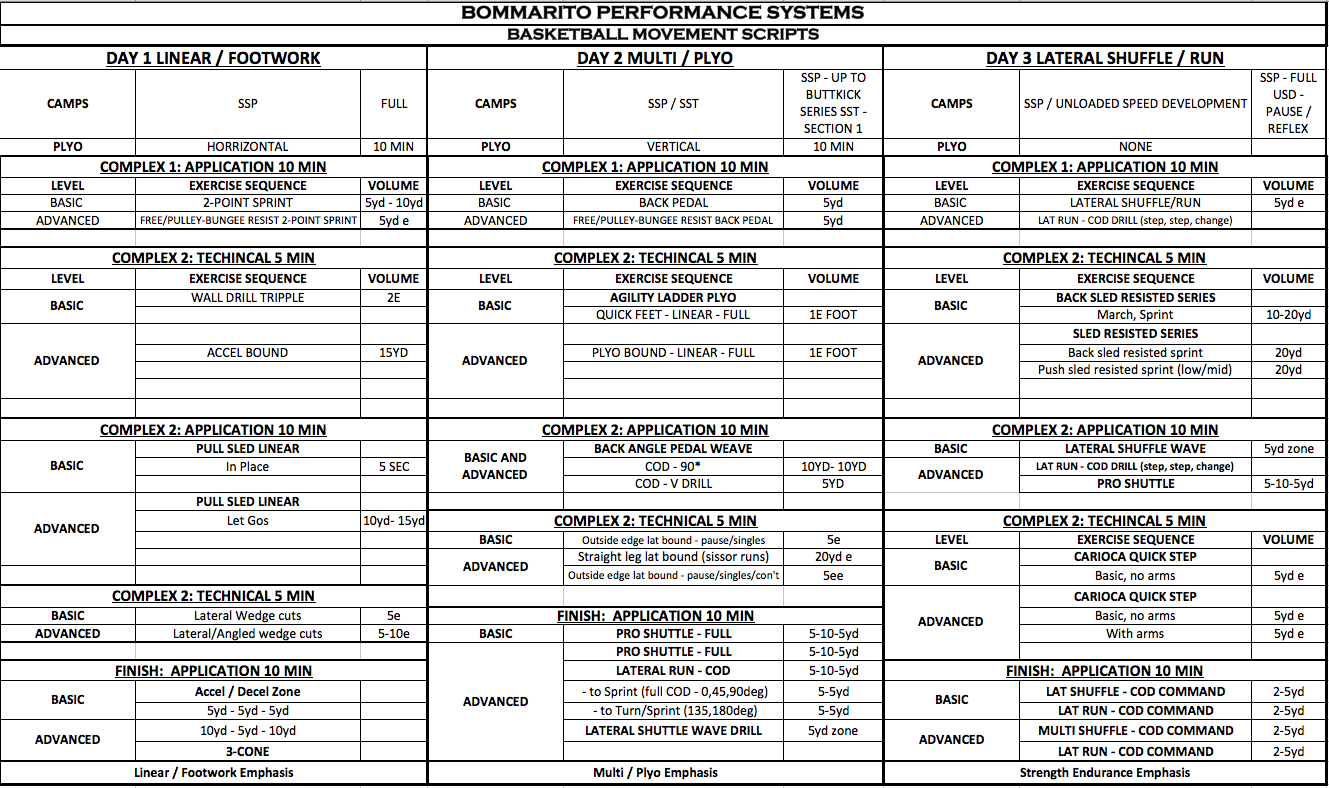
Basketball Movement Scripts
BASKETBALL MOVEMENT SCRIPTS
Within the sport of basketball, athletes will under go many movements that can be trained and enhanced. The most obvious would be jumping, running, and lateral movements. Some others may be back pedaling and arc running. This script aims to develop all aspects of basketball movements. Day1 focus on linear speed and fast footwork. Exercises like bounding, sprinting (resisted and free), change of direction (COD) arc drills, and sprinting slowing down and sprinting again. Day 2 multi-directional focus implements exercises to develop backwards movements, lateral running with COD, quick feet, single leg/ankle strength and vertical jumping. Day 3 is a heavy lateral day involving the use of lateral shuffle drills, strength endurance sled work, lateral movements to COD with lateral and linear runs. Always stick to the time allotted per complex and volume. Modify exercises based on skill level and injury status.
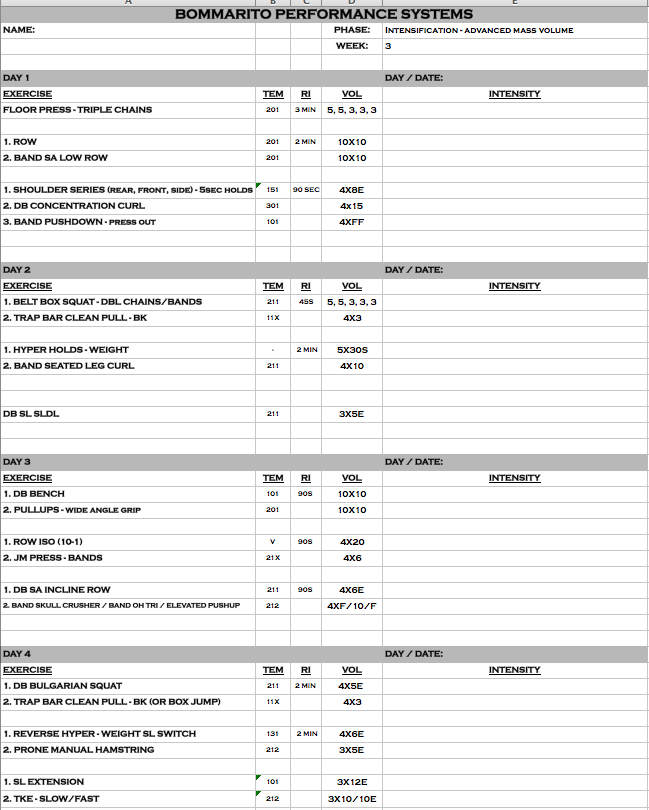
Volume Training Workout
7-8-16
Adam Boily MS, USAW, MATJS
Intensification – Advanced Mass Volume
There should come a time in most training periodization’s, where increased volume is necessary to either reinforce corrected joint alignment, increase strength past current plateaus, and increase muscle size.
First, joint alignment needs to be set through an individualized program working to eliminate bilateral differences. Typically, medical and functional evaluations are utilized to identify such imbalances prior to training. Once imbalances have been identified, corrective movements are needed to achieve symmetrical ranges of motion (ROM) for all joints. After this phase is complete, our advanced mass volume workout is a great way to increase the muscle tissues ability to avoid reverting back to unstable joint ROM imbalances through constant correct reinforcement.
The amount of sets and reps (volume) of pulling, pushing, and lifting throughout this week is designed to increase strength and size. For example, with the floor press and belt squat utilizing chains, we can ensure the variable resistance throughout the eccentric and concentric portion of the lift will increase strength past current plateaus. The chains and bands will recruit muscle fibers to contract more as the rep ends and resistance increases. Current max effort weight becomes previous max effort weight.
Some athletes require more volume than others. For them, we offer this type of workout. There may be an American football athlete that needs to bulk up such as a 215-pound linebacker that needs to be 230-pounds. Or you may have a power lifter that has reached a squat, deadlift, and/or bench plateau and requires this added volume, especially with variable resistance, to reach their goal of competing at a higher level. Always remember this workout is a template that can be modified to complement any sport. Take your workouts to the next level and mass volume train to grow your body and your potential.
Below is the advanced mass volume workout.
Elite Football Combine Prep – Strength Periodization Continued
After week 4 of draft prep training, most athletes will be due for a downloaded lift in the weightroom. With this basic download lift week, the focus is to bring the volume down for upper and lower body days. Depending on the athlete, downloading the lower body and uploading the upper body may be appropriate. During this time of the year athletes will be invited to play in collegiate bowl games. If an athlete attends this week-long game he will not lift for that week and therefore, that counts as his download week. The low volume and/or no lift, allows the body to actively recover from the previous weeks of conjugate dynamic. Upon completion of this week, the athlete will be ready to increase the strength plateau by advancing into the next strength/power and power/strength phases.
The strength/power phase focuses on a big increase in intensity with emphasis on strength slightly more than power development. The first upper body day 1, with “clusters,” increases pressing strength dramatically. Pulling and elbow extensor volume is increase for more upper body strength, power, and endurance. The lower body days are designed to potentiate power output. Many resisted jumps paired with free jumps are effective in this phase. This jumping power will also transfer to the sprint training, which is preparing the athletes to peak in a few weeks.
The following power/strength phase focuses more on power output than strength gains. The previous weeks have prepared the muscles for massive gains in hypertrophy and strength, leading the athlete to peak performance for maximum power. Upper body days emphasize pushing power and realizing new plateaus for the 225lb bench press rep test. The lower body resisted jumps and clean pulls are light to focus on potentiating power through faster movements. Then, realizing the new plateaus for the broad and vertical jumps.
The final strength phase is the max/taper phase, which focuses on upper max strength through heavy weight with a power component by adding chains. Most of the pushing is fast and pulls are reflexive. The inverted row holds are designed to isometrically strengthen the muscles that are contracted at the bottom of the bench. This isometric strength will produce a more powerful stretch reflex on a 225lb bench press rep test. The 225lb bench holds are designed to isometrically strengthen the muscles involved in keeping the bench press body position base and elbow extensors that are keeping the arms straight. This strength will allow the athlete to have a temporary regrouping moment to make sure the body is properly positioned to perform single repetitions under fatigue during the end of an actual 225lb bench press test.
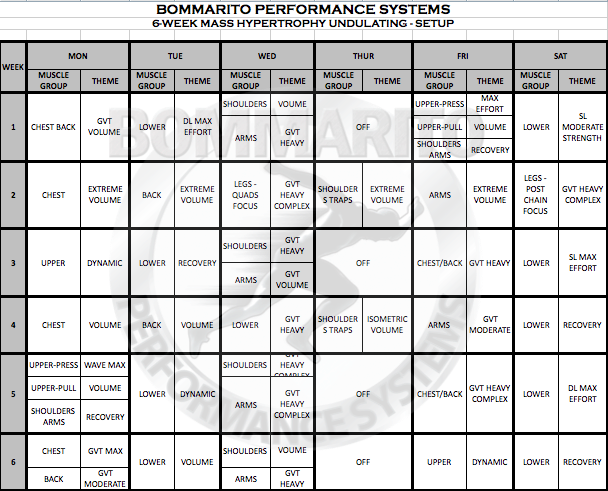
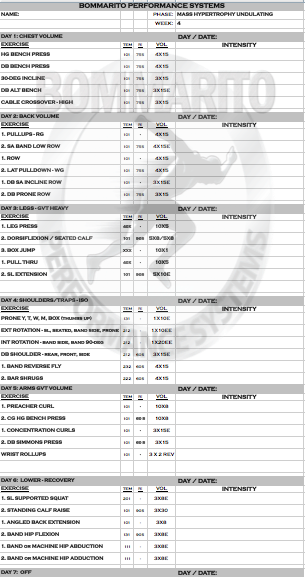
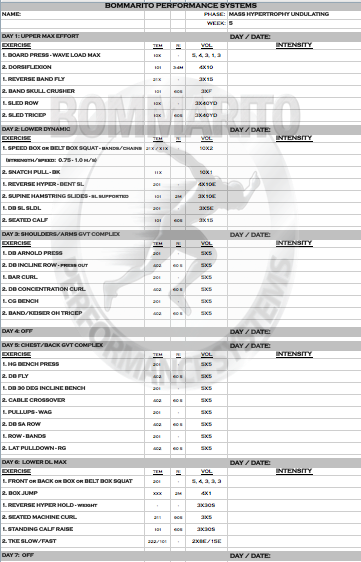
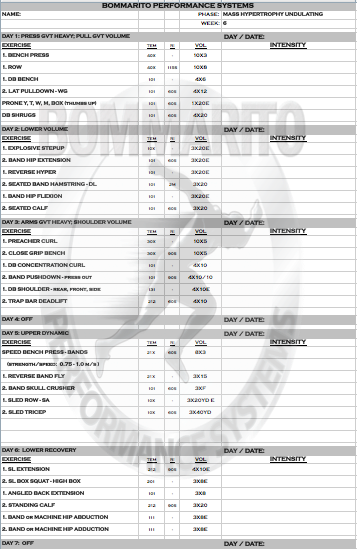
6-WEEK MASS HYPERTROPHY UNDULATING
6-WEEK MASS HYPERTROPHY UNDULATING
Pete Bommarito, MS, CSCS, USAW, MATCS
Owner/President, Bommarito Performance Systems
Owner/President, Bommarito University
Maximizing muscle growth is obviously an extremely important concept for all different types of athletes and fitness enthusiasts. There is tons of data and research that shows different types of programs, and the hormonal response associated with each. The key is to implement the research into application – but with programs that can be safely and intelligently performed that gets the desired results without running the risk of overuse injuries. Separating a person’s goals into 2 main categories is important – the general population and athletes. The benefit of this undulating program is it can be performed and be extremely beneficial to all types of general population and all athletes at various levels.
[table id=1 responsive=scroll responsive_breakpoint=phone /]
As always the exercises in this program can be referenced in the BPSU Exercise Database. Make sure you give us feedback and questions in our Forum as you go through this program!
General Population
In the general population not necessarily focusing on an athletic event, it can be purely health related and for aesthetic purposes. Maximizing hypertrophy can lead to a number of health benefits – including but not limited to joint health, structural alignment, bone health, and accelerating fat loss for overall better function.
In terms of aesthetic purposes, males typically want to build as much muscle as possible with being as lean as possible. This program will help to accomplish both. The hormonal response for males is much greater than females, so a male can expect an overall muscle growth that is greater. Keep in mind that even if a male’s ultimate goal is to get “as lean as possible without getting bigger”, this program will still work. The more muscle mass, the higher the metabolic function, which will lead to overall fat loss to be accelerated. Keeping with this same hormonal concept, women should definitely NOT be scared off from an intensive program such as this. For a woman to maximize their genetic potential for muscle growth, doesn’t necessarily mean that they will “get bigger”. The “toning and definition” that I hear women talk about when discussing overall goals of a fitness program WILL BE accomplished with this type of program. Remember that a women’s overall hormonal response is just different than males. Meaning an intensive hypertrophy program will stimulate muscle growth so the muscle can actually be seen more prominently – hence, the “toning and definition” they crave. Couple this concept with the increase in metabolism and thus accelerating fat loss – and women can definitely accomplish their goals – mainly maintain weight but lose fat and gain the toning; OR even lose weight but still have that lean and defined look.
Athletes
The other positive about an intensive program such as this is that it can be used for all athletes, without compromising their overall goals of being explosive. Even an athlete such as a body builder, model, or fitness competitor can benefit tremendously with this type of an undulating model. Many times if an athlete like a body builder is trying to build as much muscle as possible, they get locked into high volume, longer tempos (speed of repetition), and short rest periods. Which is fine, because that is what the research tends to dictate. However, there is nothing wrong with occasionally shifting towards to neural component of maximum effort work and maximizing motor unit recruitment. In a sense, “getting stronger” from implementation of max effort work into a microcycle like this, will allow for greater loads to be placed on the actual “volume days”. If the volume days can be accomplished with these great loads because the athlete is actually stronger, the hormonal response can be elevated with these days – hence more muscle growth.
For traditional sport athletes, this undulating model is a phenomenal method to maximize size and strength, without compromising speed and power. The old way of thinking of “if you train slow you will be slow” can be interpreted in many ways. Hitting an aggressive 6-week microcycle like this to elicit as much muscle growth as possible will definitely not compromise the overall expression of power – especially when you think about how many other microcycles can be placed into an off-season that focuses on power and power endurance. Shifting the focus onto muscle growth for a short 6-week microcycle can really set a great base of size and various types of strength and strength endurance. This base can lead to more efficiency when the focus shifts over to a microcycle that focuses more on maximizing power. This is especially true when you consider the undulating model – note that there is still dynamic and explosive work strategically placed throughout the cycle.
Recovery
This could be the most important factor in the overall success of this model. Note that there are recovery days and off days placed into the workout. Because of the extreme time-under-tension on some of the heavy volume days, recovery is extremely important to allow the muscles AND the nervous system to adequately recover. This single biggest mistake made when attempting a cycle focusing on hypertrophy is that recovery days are limited or eliminated.
Recovery days doesn’t mean that the training stops, or lighter loads/intensities are even implemented. It’s just more of a focus on single joint work, lower overall volume, and controlled, focused tempos. This is necessary not only to allow recovery – but also (and probably more importantly) to keep the structural balance of each joint. This structural integrity will actually allow for more success during the heavier or higher volume days focusing on multi-joint lifts. Think of it in these terms: A multi-joint press will involve elbow extension. A multi-joint pull will involve elbow flexion. A multi-joint squat or single leg squat will involve knee extension and hip extension. It’s always beneficial to ensure that the individual segments are a strong as possible to allow for more overall efficiency (and less compensation for weaker segments).
Undulating Methodology
The overall model of “undulating” is really dominating the research. Meaning that each week doesn’t have a particular focus – each day of each week consistently switches the focus. This allows for an efficient rotating shift between neural (max effort), cellular (volume), combination (more time under tension with maximal weights), and recovery (segmental strength). Even “dynamic” or power based themes are placed into the rotation.
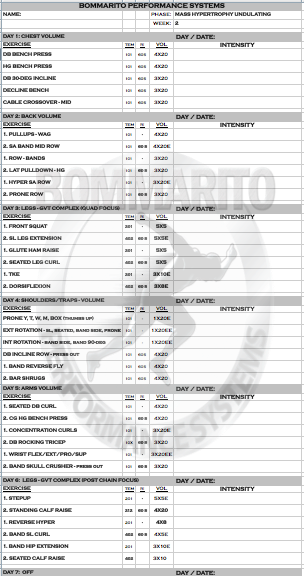
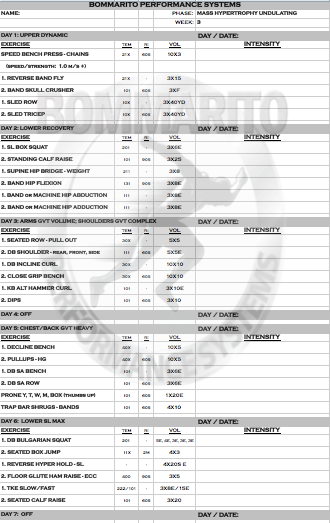
The research consistently dictates that in order to optimize the neural recruitment on a max effort day, hitting this type of workout every 10 days is necessary. Research also dictates that a high time-under-tension (longer, slower repetitions) coupled with shorter rest periods will optimize the hormonal response for muscle growth. Note that some days, a particular muscle group is the focus with this exact concept implemented – this is greatly exemplified in weeks 2 and 4. Some days, a complex (or superset) is implemented – usually in the form of a variation of GVT (or “German Volume Training”) model. These GVT days can be with volume (example week 1, day 1); max effort work with higher tempos (example week 3, day 5; or week 6, day 1); or even complexing single joint and multi-joint lifts for overall volume (example week 2, days 3 and 6). This type of consistent rotation of cellular (volume) and neural (strength) components will help maximize ALL expressions of hormonal response – which can allow for greater recovery, but ALSO greater overall muscle stimulus
Workouts
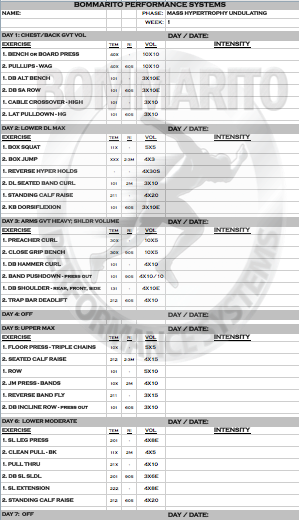
As with all BPS programs, the when writing with a “1” immediately followed by a “2”, this is an immediate complex (or superset). Taking week 1, day 1 as an example:
The “1” exercise Bench/Board Press with a 40X tempo with 10×10 volume. The “2” exercise below it is Pullups – WAG (wide angled grip) – also with a 40X tempo and 10×10 volume. Note there is not RI (rest interval) for the Bench/Board Press, but there is a 60 second rest interval for the Pullups. This means that a set of 10 (40X tempo) of Bench/Board Press will be performed; then IMMEDIATELY perform the Pullups (40X tempo) for a set of 10. Then rest 60 seconds. Then repeat that exact sequence for 10 total sets.
The Setup illustrates the overall periodization of the 6-week cycle. Note that each day of each week will have the muscle group focus along with the theme. The Theme of each day is also listed at the top of each day within the actual workout.
Implementation of Speed/Movement Work and/or Cardio Work
Each person is going to respond differently to this aggressive type of loading – so general rule of thumb is to listen to the body, and DON’T push through extreme fatigue and soreness. In terms of other general rules to follow
- Don’t hit any aggressive “application” methods of speed during this cycle (like over-speed or long absolute speed) or high-loading change of direction drills
- Focus more on technical aspects, linear acceleration, and multi-directional runs (not changing directions)
- Perform High Intensity Interval Training type of cardio on upper body days
- Perform Long Slow Distance type of cardio on lower body days
- Definitely do not do any type of boxing or grappling type of conditioning on the upper body days that is max effort, or extreme volume
MAXIMIZING YOUR WORKOUTS ON THE ROAD OR AT HOME WITH LIMITED TIME/EQUIPMENT – THE VARIABLE LOADING AND BODY WEIGHT SYSTEM

MAXIMIZING YOUR WORKOUTS ON THE ROAD OR AT HOME WITH LIMITED TIME/EQUIPMENT – THE VARIABLE LOADING AND BODY WEIGHT SYSTEM
Pete Bommarito, MS, CSCS, USAW, MATCS, MAT Jumpstart
In order to really maximize your training for yourself and/or your clients, having the structure is always the key. The optimal structure can be centered around a number of aspects:
- Medical disciplines to treat and evaluate pre/post
- Facilities and equipment the can maximally facilitate individualized goals
- High level trainers/coaches and/or training partners
- Optimal time for preparation, rest periods, and post recovery
- Nutrient Timing
- Proper sleep, recovery, hydration, and stress-free personal environment
It is clear that one or more of the aforementioned aspects are just common parts of most people’s everyday lives and they will always compromise “optimal development.” This is especially true for those that travel frequently, or just simply for those clients that have so many personal responsibilities with family and/or young kids that it might be logistically impossible to get to a facility with the necessary amenities and equipment. Planning for these logistical factors is always a good idea; as some development (even if it is “sub-optimal”) can be better then no development at all. As long as trainers/coaches and the clients have a full understanding that this can’t be setup as a standard for people that are just too lazy to commit to what is optimal at least part time. It is simply great sample general plans that can keep the development going during these types of tough situations.
From an athletic perspective, tennis is a great example. There is no way that an elite tennis player can have a perfect plan on the road to different countries and absolutely ensure that there is a facility in close proximity that has all of the adequate equipment and services. Further, there is always a financial factor – some players can surely bring a “travel performance coach” on the road; some can’t. In either case, the coach MUST plan for implementing a program when traveling with the client; OR give the client solid education and a program to take on the road. And this implementation must be planned for a “worst case” scenario.
From a general fitness perspective, the best trainers are not just the ones that can directly train a client adequately. It’s the education of what to do in a “worst case” scenario if your client needs to travel, has an emergency, or has a logistical issue like family issues that inhibits the ability to attend sessions.
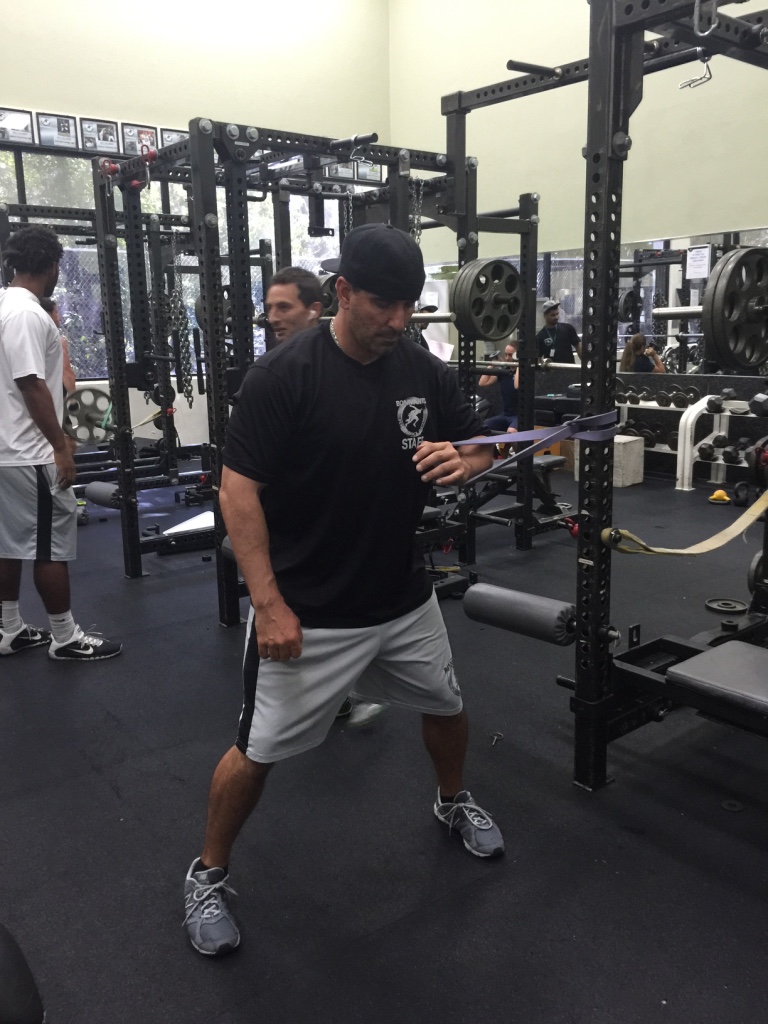
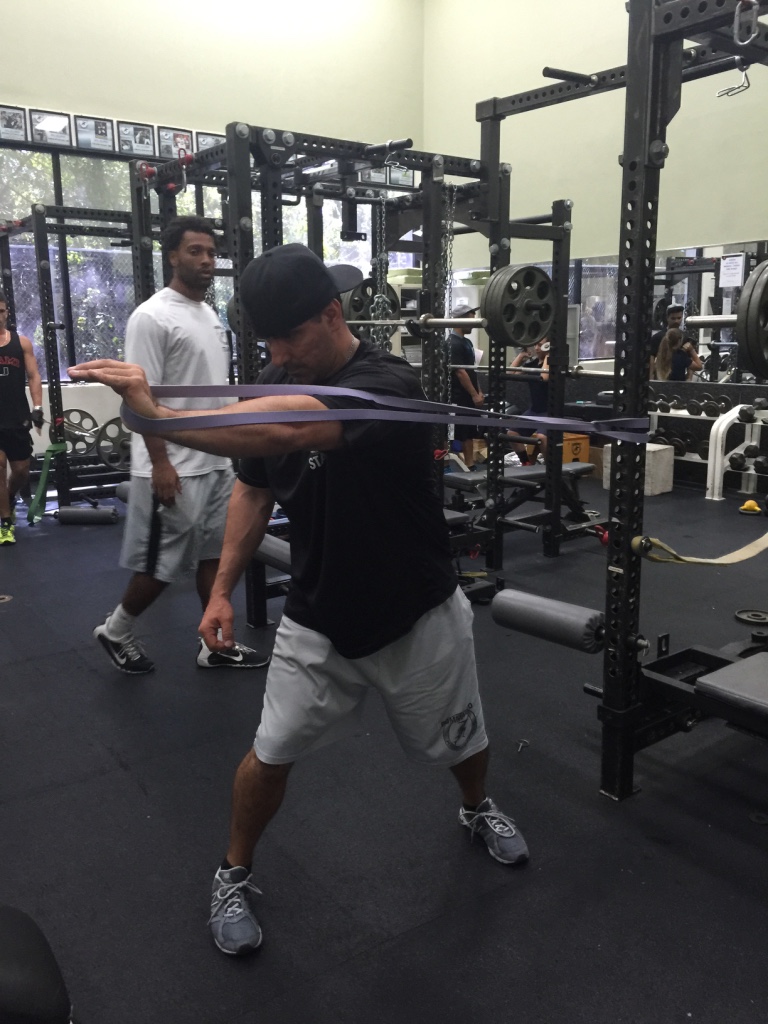
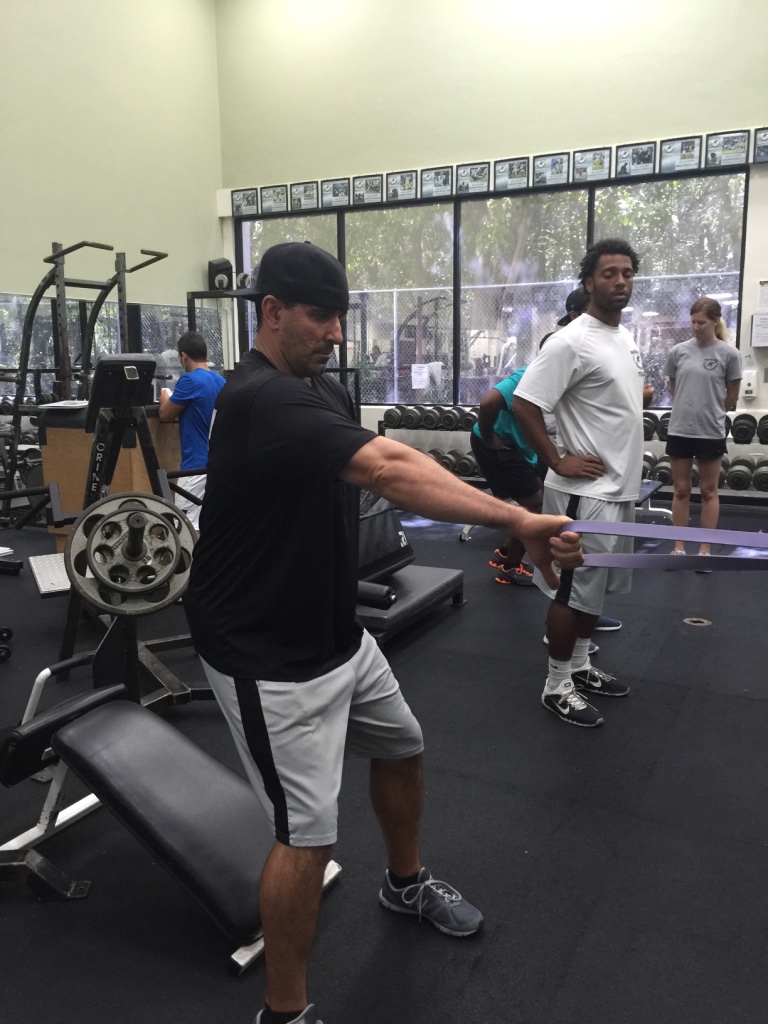
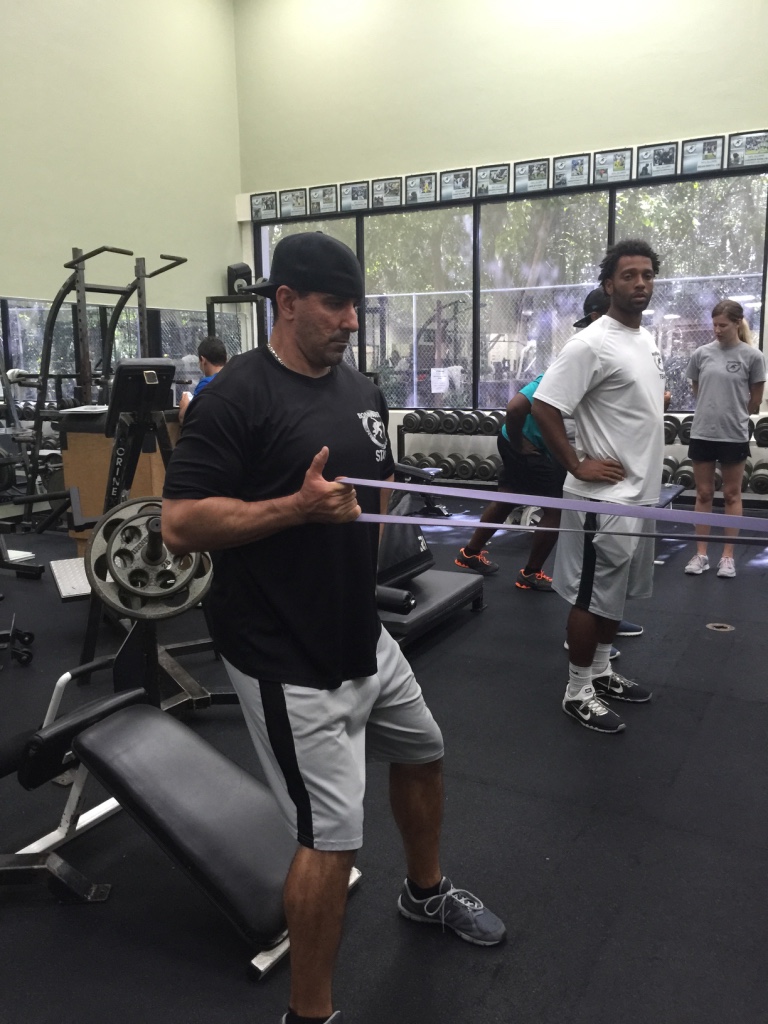
In any of the above scenarios, body weight training and band training is a great place to start. There are many different modes of training, but body weight and bands can usually be the best system to implement because of the ease of implementation with no “facility”. It’s easy to travel with, it’s inexpensive, and the overall variety of exercise implementation can really facilitate a solid, scientifically based program.
EQUIPMENT
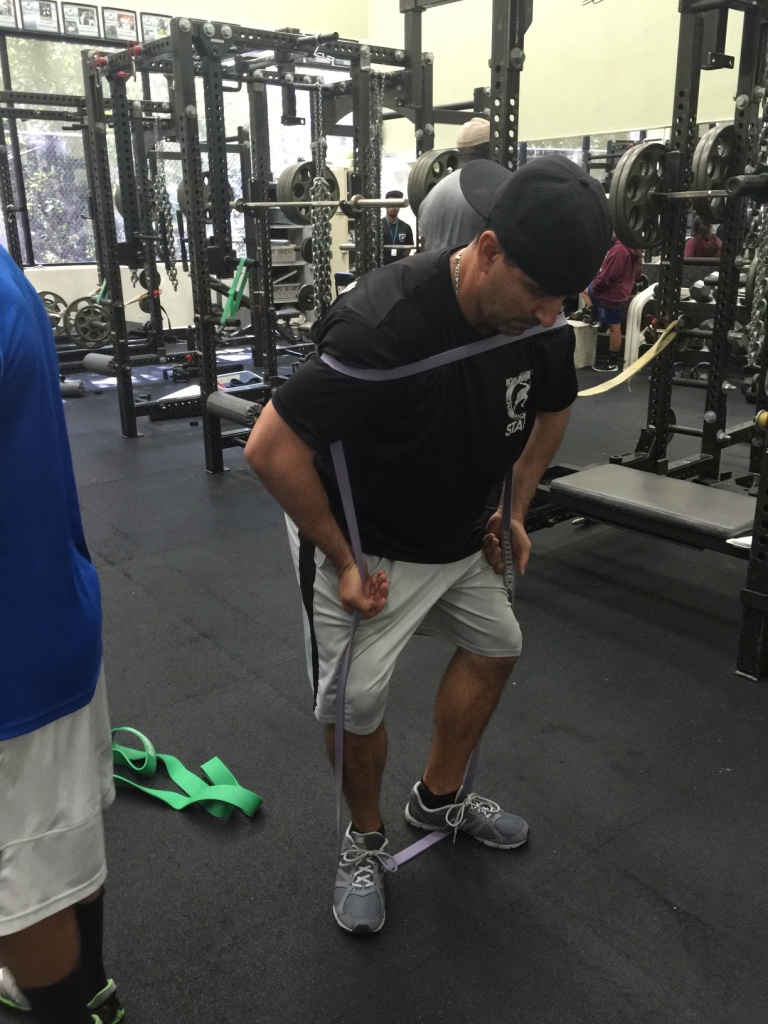
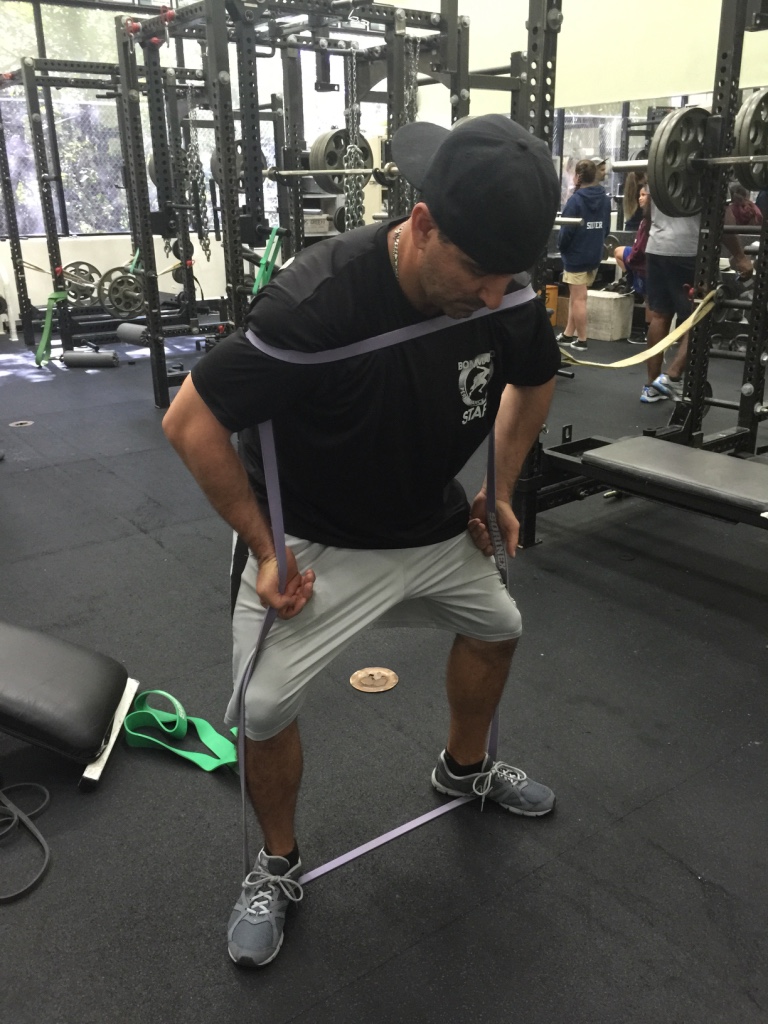
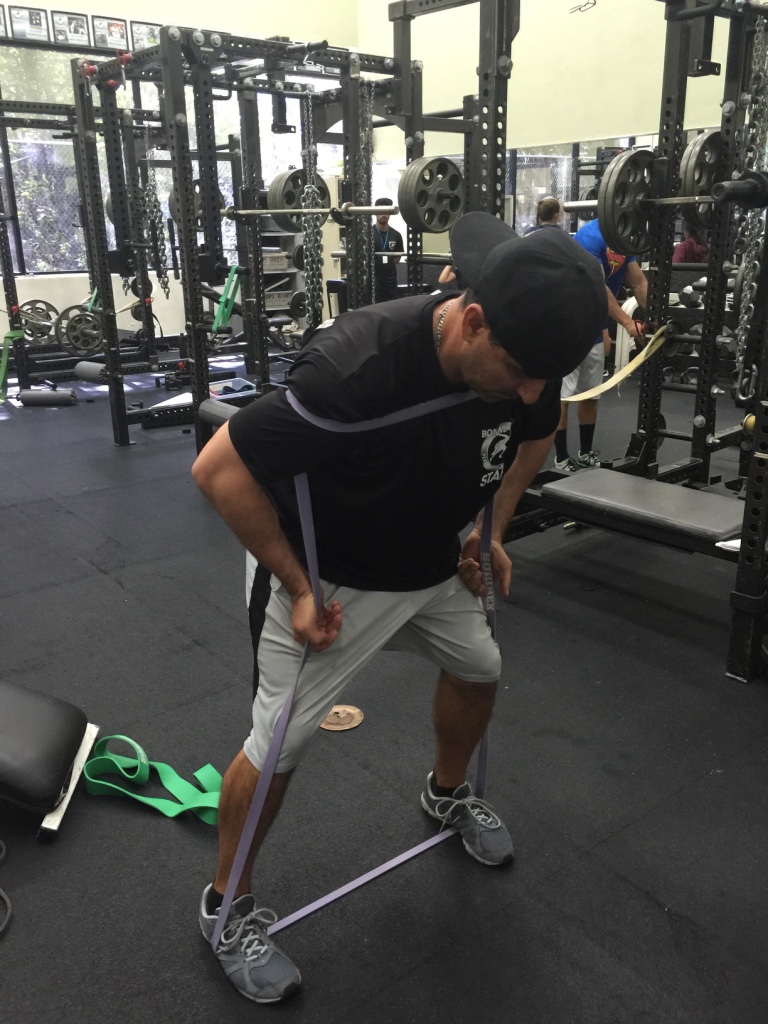
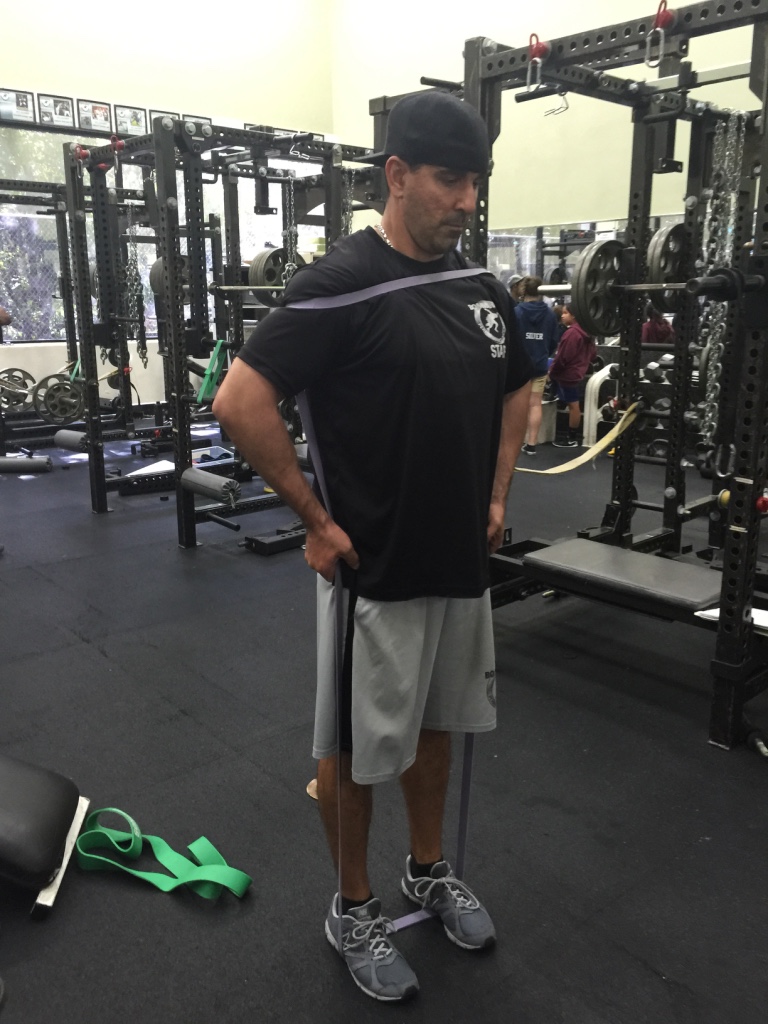
Sorinex Bands – Mini, Monster-Mini, Light, Medium, Heavy
EXERCISE DATABASE
Upper Press
- Band SA Punch
Staggered Stance SA Band
Rotate SA Band Punch
Variations
- With Protract at end of Punch
- Band DA Punch
- Staggered Stance DA Punch
Upper Pull
- Band SA Row
Angled Stance SA Row
Reverse Band Fly
Variations
- High
- Low
- DA Row from varying positions and angles
Upper Auxiliary
- Band Tricep Pushdown
Band OH Tricep Press
Variations
- SA Tricep – varying angles
- Reverse Grip Tricep – varying angles
- Band Tricep Press – chin
- Band Tricep Press – forehead
- Band Bicep Curl
- Band SA Bicep Curl
- Band Hammer Curl
- Band Wrist Flexion/Extension
- Band Front Shoulder Raise
Band Side Shoulder Raise
Band Rear Shoulder Raise
Variations
- Front V Raise
- Front V-Y Raise
- Side Raise – Shrug
- Heavy Band Shrug
Lower Hip/Quad Dominant
- Band DL Squat
Band Bulgarian Squat
Variations
- DL Squat to OH Press
- Lateral Walk to Squat
Lower Posterior Chain
- Band Pull-Through
- Band Seated DL Curl
- Band Seated SL Curl
- Body Weight Hip Bridge
- Variations
- Hip Bridge – Dorsiflexion or Plantarflexion
- Hip Bridge – knees/feet in; knees/feet out; knees in/feet out; knees out/feet in
Lower Single Joint
- Band Hip Flexion
Band Hip Extension
Band Hip Abduction
Band Hip Adduction
Variations
- Band Hip Flexion w/ abduct or adduct force (angle the band)
- Band Hip Extension w/ abduct or adduct force (angle the band)
- Band Hip Abduction with flexion or extension force (angle the band)
- Band Hip Adduction with flexion or extension force (angle the band)
- Band Lateral Walk
- Internal Rotate feet
External Rotate feet
Neutral feet
- Standing Calf Raise
- Sraight Leg Neutral Feet
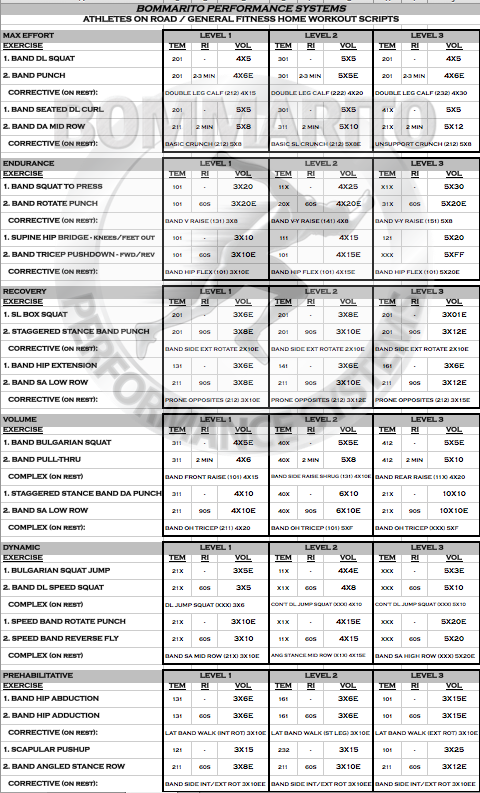
WORKOUTS
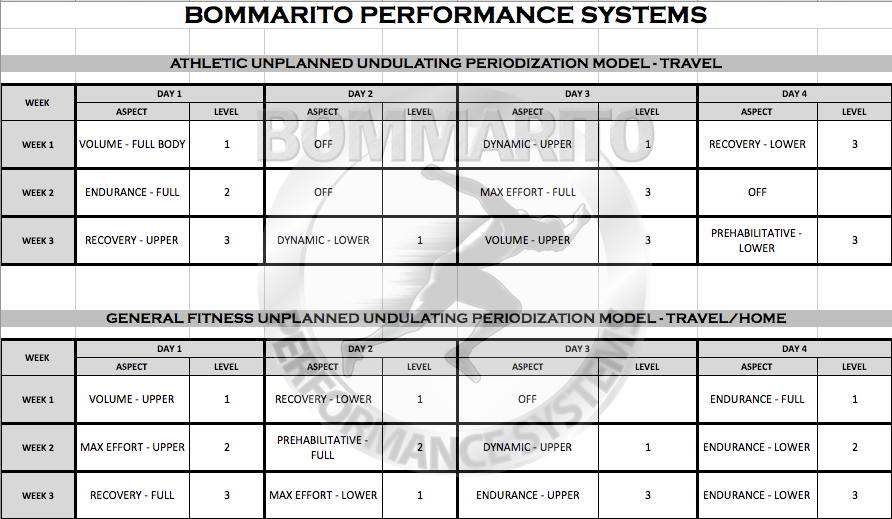
Using the listed workout scripts as general templates, it can be easy to construct an undulating periodization model. This model should always be with the understanding that it should be unplanned. This is especially true for athletes on the road. If an athlete is on the road with heavy tournament play, the training should supplement practice and match play – not interfere with it. It’s virtually impossible to perfectly plan the recovery from practice or an event. The basic way to plan a workout script is to go off the “readiness to train” of an athlete. Simply how the athlete feels, soreness levels, energy levels, etc. For advanced athletes with a better understanding of their body, or if athletes have access to Neuromuscular Therapists, it becomes a lot more detailed in terms of the actual appropriateness of the workout selection based on neural capacity and function.
Note that each workout has 2 complexes. The “1” exercise is always immediately super-setted with the “2” exercise, then given rest period will take place (noted by “RI”, or rest interval, on the script). The rest period can be a simple inactive recovery. Or there can be a chosen “Corrective Exercise” chosen during the rest interval. There are many sample corrective exercises listed on the script. For example, on the MAX EFFORT scripts, a Double Leg Standing Calf Raise is listed as a sample exercise during the rest interval of the first complex. Because the muscles involved in plantar flexion are such a crucial component of the gait pattern (especially from the complex an specific pronate to supinate action from absorbing to re-directing force), it can be a great chosen exercise during this rest interval that can assist with “correcting” dysfunctional gate patterns (of walking, or dynamic motion and changes of direction). Note the progressive overload between the levels. If there is a specific inhibition that got activation from a therapist, a specific isolated exercise can be used to facilitate a progressive tolerance to force at that joint/muscle. If there is no set pattern of specific evaluations, the listed exercises can be great choices – because they are globally seen as assisting with many general dysfunctions seen in many people – athletes and general fitness clients.
For simplicity purposes, all of the listed workout scripts were constructed with “full body” on each day. However, if there is a week where it is appropriate (based on response) that 3 or 4 days can be used, an upper body or lower body day can implemented using the same model. So if an upper body day needs to be substituted for a full body day that is listed, both complexes can have a “1. Push to 2. Pull” system, with a rest interval that contains a corrective.
Also note that some of the Rest Intervals contain “Complex” instead of a corrective. An example would be the VOLUME day. Instead of focusing on an exercise assisting with the force at a specific or a general dysfunction, this is an exercise that completes the overall complex. Hence, the VOLUME day is an intense continuous workout with little to no rest.
As with anything in Sports Performance or General Fitness, it’s still a good idea to plan based on the predicted response – but always CHANGE THE PLAN based on the actual response. With these points in mind, these examples could be appropriate periodization models for an elite athlete on the road, or a general fitness client that needs a good “home workout” for a period of time:
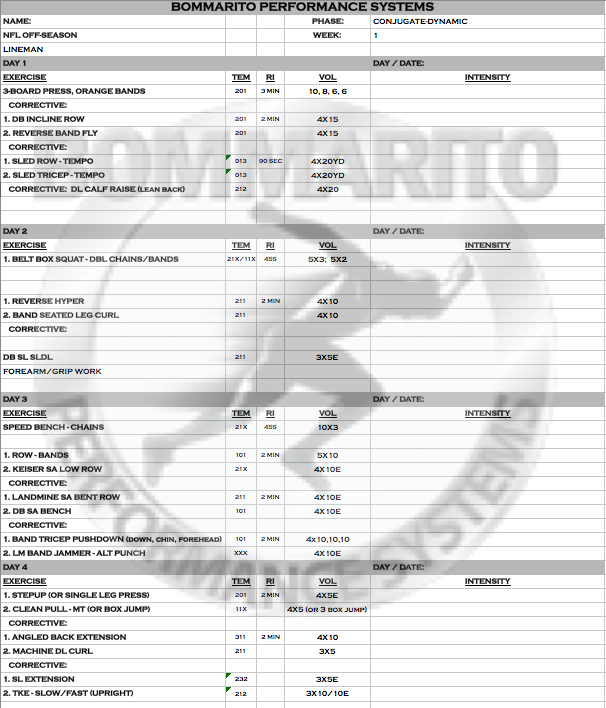
ELITE FOOTBALL OFF-SEASON STRENGTH PROGRAM
ELITE FOOTBALL OFF-SEASON STRENGTH PROGRAM
Pete Bommarito, MS, CSCS, USAW, MATCS, MAT Jumpstart
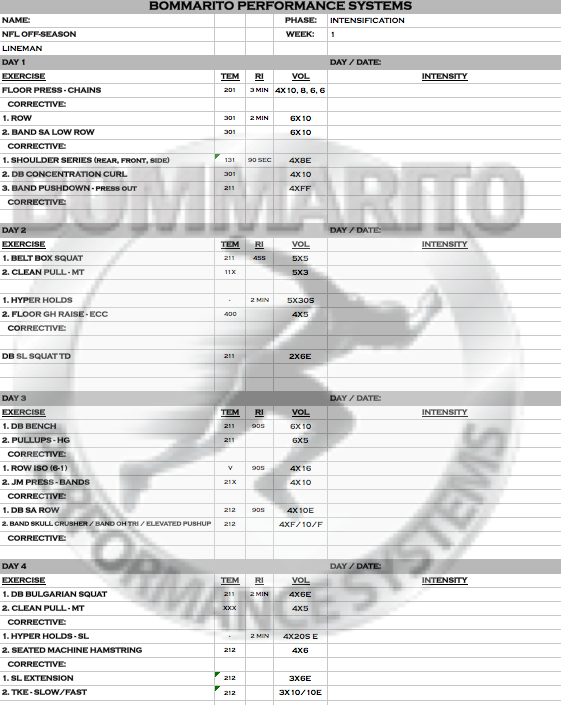
Elite status in football can be categorized as any fully-grown elite high school player that has years of strength training experience, a collegiate player, or a professional player. While this program was designed specifically for Lineman, it has been also utilized for skill players needing to add muscle, strength, or a combination of both. It is one of the more aggressive programs designed in terms of overall volume and a progressive intensity with variable loading and speed strength development. It is also very sport and position specific, especially at positions like Lineman that hit on every player and have to grapple a lot. Note that the overall theme, especially in the Intensification phase, is a lot of work on the upper Posterior Chain. This type of intense and high volume mass/strength building is essential for extreme contact athletes like Lineman.
INTENSIFICATION
With football, we usually undergo two different Intensification phases throughout an off-season. First, after a brief GPP phase after the season. This Intensification phase is usually pretty standard – normal progressive increases of volume and intensity to set the base for speed-strength work before OTA’s or Spring Ball. Once the summer hits and preparation for camp ensues, we usually have 7-9 weeks total. In this time block, an aggressive Intensification exemplified here is more applicable. The base is already set; a good microcycle of speed strength and power is already peaked before OTA’s and spring ball.
When coming out into the summer, we’ve had good success with hitting really high volumes in an elite Intensification phase. Note that some of the posterior chain work of the upper body even has a “German Volume” feel to it. These concepts used for the German Olympic athletes that have been widely popularized in the American Bodybuilding culture, really apply to this phase.
Week 1
Note that the upper body is split into moderate strength in Day 1, German Volume Training GVT of upper pull on Day 1; and a push/pull complex of GVT in Day 3. There is also a pure strength split of the lower push series of double leg on Day 2 and single leg on Day 3. The lower posterior chain work is heavy into isometrics, and eccentric loading.
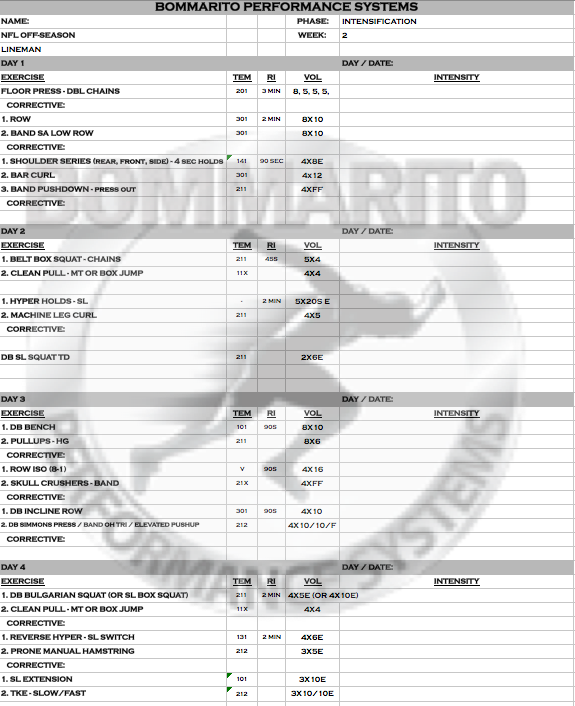
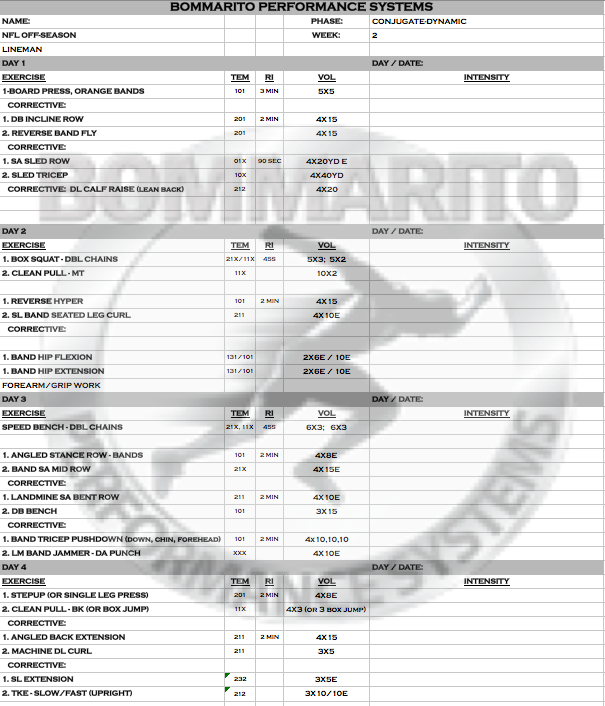
Week 2
Note the progressive overload from week 1. The upper body progresses into lower volume / higher intensity, with more variable loading. Using multiple chains on a partial pressing such as a floor press really helps with accommodating resistance as more max strength is built. The GVT complex on Day 3 is also progressed with volume. Also note that the shoulder strengthening is progressed by isometric strengthening volume (131 tempo in week 1 to 141 tempo in week 2). Note that the posterior chain lower is still focused in isometrics, but a different, more advanced stimulus is now created with the SL holds.
Also note that the Olympic lift partials are still complexed with the lower body DL/SL split between days 2 and 4 – really pushing the limits of Post-Activation Potentiation of pure power development.
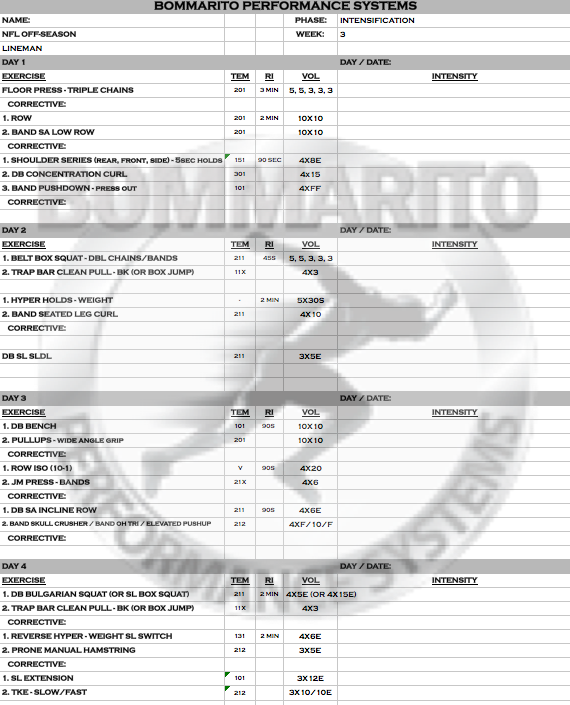
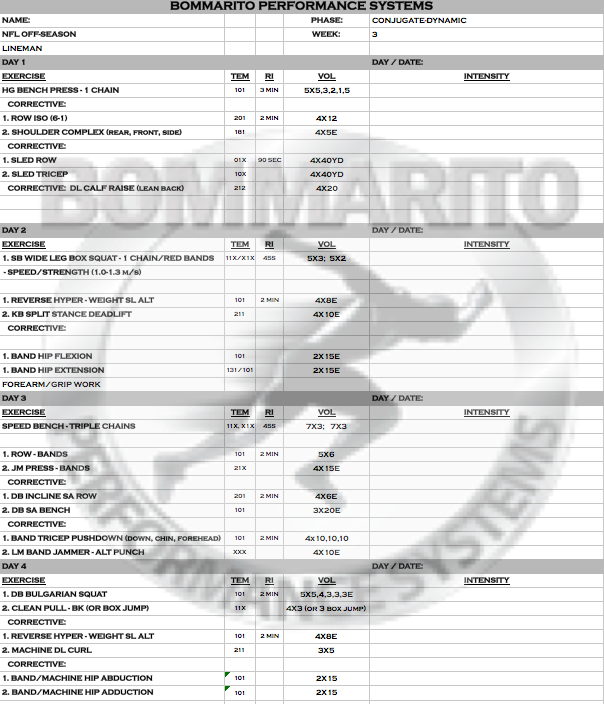
Week 3
The progression into pure maximum strength is now complete – with intensity progressing above 90%, and again an overload with increased variable loading moving into triple chains. At this point, some of our most advanced Lineman and experienced lifters even progressed into 4 and 5 chains each side. The push to standard GVT push/pull split is complete on Day 3, with 10×10 on each. The lower body really focuses on max strength on both the DL and SL lower body days. Note that this is so aggressive, that some players needed to do more of a recovery day on Day 4 (see the body weight SL box squat option).
CONJUGATE/DYNAMIC
This phase is definitely a favorite of ours with regards to building speed-strength, strength-speed, and peaking power at the end of the microcycle. As opposed to doing a typical max strength / speed-strength split with upper body, the focus is more on resetting the pressing volume of moderate strength, pure strength, and maximal absolute strength between Day 1 of all three weeks. Note the variable loading has now progressed into bands on the “strength” day 1. Also, with regards to speed-strength or strength-speed: the tempo still follows a standard 21X on the first week. It’s essential to keep building eccentric loading and isometric pause into pure concentric power. This type of overload will progress efficiently into a dynamic eccentric on the dynamic day; if the athlete is ready for it by weeks 2 or 3.
While this might not follow exactly into the standard “Conjugate-Dynamic” microcycles popularized by the Powerlifting community, it has very similar concepts. It’s important to understand that the concepts can be similar; but the progressions and exercise selection needs to be modified to a football players that may have injuries and/or wear and tear coming off a season and/or OTA’s/spring ball.
Week 1
This week is focused on moderate strength of the upper body with variable loading, followed by heavy volume of pure concentric work with sled rowing/tricep work. Note that the most efficient way to really begin the speed-strength work on day 2 lower pressing is to stay consistent on the belt squat from a box. The max effort work on lower body is typically SL work. For some lineman that are aligned properly and need to add muscle/strength, we do some DL Olympic squats in place of this SL work.
Note that the posterior chain work has now progressed into standard tempos of concentric/eccentric strengthening of Hypers and Back Extensions. If the posterior chain is strengthened enough isometrically in the Intensification phase, this can be an intelligent progression.
Week 2
The progression of upper body pure strength (exemplified with the 5×5) also increases the range of motion by progressing from a 3-Board Press to a 1-Board Press. The sled work now builds volume and concentric power with the 01X tempo on the rows and tricep work.
Also note the progression on the dynamic days of upper and lower body. The 21X tempo progresses into a 11X tempo (and even an X1X tempo for more advanced lifters).
Note that the lower posterior chain work is moving toward a reverse periodization model. The volume is increasing as more strength is built in all phases.
Week 3
Wave loading is a great concept to push the limits of pure maximal absolute strength in the upper body. Note this loading pattern on the pressing strength of Day 1. There is also an increase of volume of the sled work.
Both of the upper and lower body dynamic days should have progressed into a solid X1X tempo by this point. The Upper body might have even progressed into an XXX tempo for advanced lifters at this point. We tend to be careful of XXX tempos on squatting motions, as the isometric pause is still to valuable to be able to unload the knee joint, and ensure proper intention on the dynamic concentric action of the squat. The dynamic days also really intensifies with heavy variable loading of multiple chains, or bands+chains. Also note that the focus has now shifted to Speed-Strength, with a tendo marker of 1.0 to 1.3 m/s.
There is also a heavy focus on single joint hip work. This type of alignment training is essential to all weeks for skill positions. It really assists the proper joint symmetry of all of the heavy lower-body work in this final week for Lineman.
ADD SOME VARIETY TO YOUR TRAINING
By Pete Bommarito MS, CSCS, MATCS, USAW, MAT Jumpstart
11/11/14
We’ve been approached by countless people over the years with the same standard questions about fitness, training, and overall health. These questions get asked by everyone: people who train themselves but are advanced and experienced, beginners looking to get started, even high level athletes.
1. What is the best way to lose weight?
2. What is the best way to get toned?
3. What is the quickest way to get “in shape” for just general, overall good health?
There is countless ways to answer those questions. However, one specific answer that will relate to all of the above “common questions” – Power Endurance and Variety within the Power Endurance cycles.
Power Endurance
Strength can be easily understood by how much weight can you lift. Power is how fast you can lift a particular weight. Power endurance is how long can you sustain a particular level of power output. It has been proven in numerous scientific studies that Power Endurance intervals is the most efficient way to lose weight, get toned and increase our overall cardiovascular fitness.
For all you people that are timid of “lifting weights” or you just prefer alternative exercises: your body weight is a weight (hence, body weight exercises can be very effective if done properly); a resistance band is a weight; air resistance (like on the KEISER machine) is a weight. These types of weighted resistance can be very effective at providing good solid intervals for Power Endurance.
There are literally thousands of exercises that can be done for power endurance with body weight, air resistance, and bands. We are going to focus on three effective exercises that can be incorporated into any Power Endurance Circuit
Keiser High Rotation
Set a comfortable resistance, choose a power output level, and then try to maintain a certain percentage over time. All of this can be seen on the digital readout on the Keiser Machine.
From the start position, drive through the resistance in the rotation shown as fast as possible, return to the to the start position and repeat.
Time on: 30 seconds
Time rest: 30 seconds
Total sets: 10-20 (5-10 each side)
Band Low Row
Choose a resistance band that you can comfortably perform the low row action with maintaining good form and proper posture. Set the resistance level accordingly (how far you anchor the band to your body). From the start position (thumb down), quickly row the band towards your body rotating your thumb up. When the hand touches your rib cage, return to start position and repeat.
Time on: 10-30 seconds
Time rest: 30-60 seconds
Total sets: 10-20 (5-10 each arm)
Body Weight Explosive Step
Choose a box or bench height that you can safely perform the Step-Up action. From the start position, place your foot flat on the box (careful not to lift your heel), and then explosively step up onto the box/bench while driving your opposite knee up. Return to the start position and repeat. Alternate your arm action into the “running motion” as you perform the step up and return.
Time on: 30-60 seconds
Time rest: 30-60 seconds
Total sets: 10-20 (5-10 each leg)
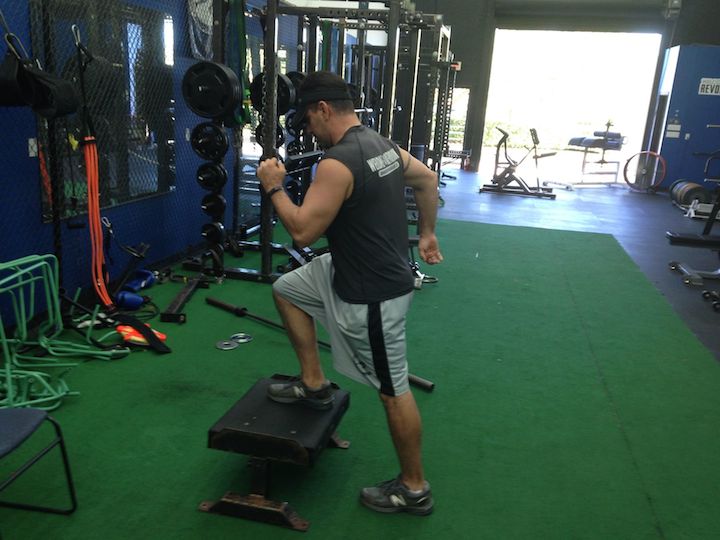
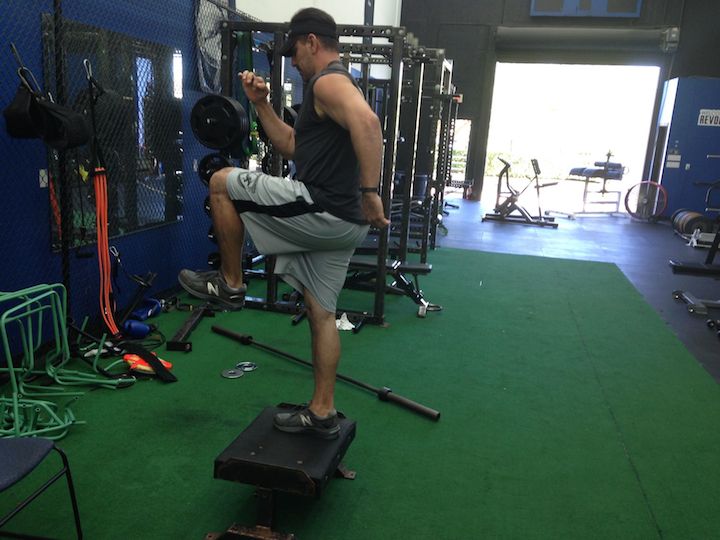
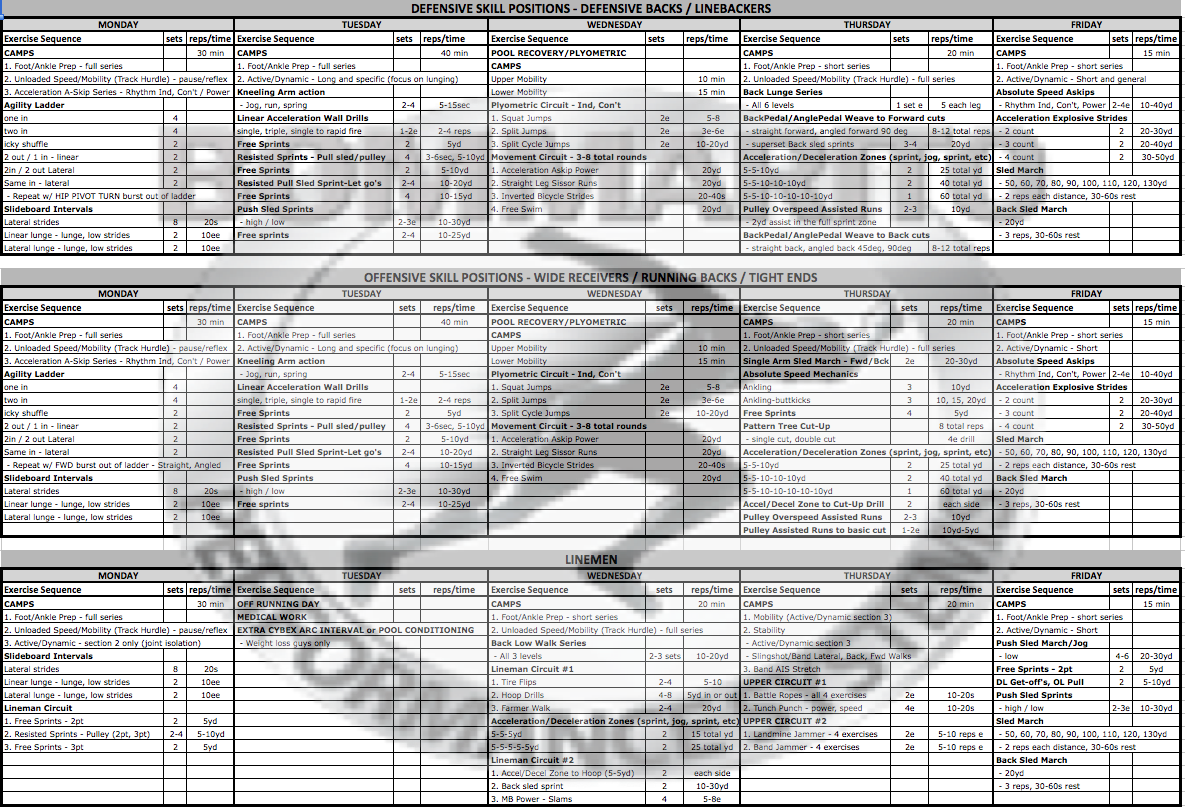
ELITE/PROFESSIONAL FOOTBALL OFF-SEASON MOVEMENT, SPEED, AGILITY, FOOTWORK, METABOLIC CONDITIONING
(TRAINING CAMP PREPARATION PHASE)
Pete Bommarito, MS, CSCS, USAW, MATCS, MAT Jumpstart
Typically for football players, the off-season is set around 4 primary phases/macrocycles:
- General Preparatory / Re-Alignment / Regeneration – immediately after the season that focuses on low volume and full recovery from the season
- Intensification – Preparation for spring activities centered around on-the-field football work
- Spring ball, OTA’s, and/or Mini-camps – low volume of maintenance work as the focus shifts to football
- Training Camp / Season Preparation – secondary intensification that increases volume again, gets into more sport-specificity, and peaking of maximum power
This article and accompanying Training Script (available on Bommarito University: http://www.bommaritoperformance.com/workshops/bps-university/) will be centered on the 4th primary macrocycle of the off-season. It’s understood that the spring football activities will affect each player individually, so there will be varying levels and time commitments that focuses around the regeneration part. Typically, this regeneration focus is much less than right after the season, as the ground base of work and the foundation for joint integrity has already been set in the first two macrocycles, and maintained as much as possible during the third macrocycle. Once the athletes are ready to get back into intensified work, this plan has proven to be extremely effective.
A full breakdown of the volume and type of work done each day of the week needs to be understood:
MONDAY – CNS ACTIVATION AND PREPARATION DAY
- High Neural loads
- Low Joint loads
- CAMPS (CNS Activation and Muscle/Joint Preparation Systems)
- Absorption Force, Accepting body weight, Re-directing force – high volume/intensity
- Unloaded Speed – low volume/intensity
- Overall Training Volume – medium to low
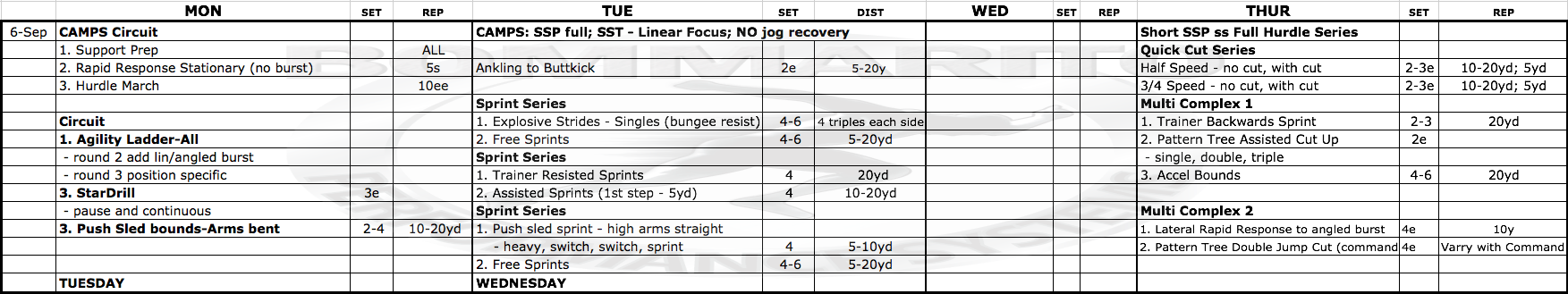
Because of the 2 days on the weekend of rest and recovery, getting the nervous system back into a heightened state is necessary to have an efficient training effect for the rest of the week. Note that there is a heavy emphasis on footwork. Footwork is about as non-sport-specific as it gets, because the body is not really moving at speeds seen in sport, hence the low joint loads. If a full-speed sprint is performed, the body can be moving at 20+ MPH, which puts a tremendous load on all of the joints in the body upon ground contact. Which is a great training effect, but not as appropriate when the CNS is in more of a suppressed state because of the 2-day recovery weekend. Remember when executing a full speed sprint, the leg moves at dynamic speeds through Recovery and Ground Preparation phases with a powerful stretch-reflex during Transitional phase on each stride. Many drills can express a similar limb speed and can be executed without the extreme joint load during the Ground Contact phase during a maximal sprint. Examples are drills like Linear Acceleration A-skip, with all 3 aspects – Rhythm Individual, Rhythm Continuous, and Power. Note that this day is heavy volume of those types of drills, especially with offensive and defensive skill players.
Another aspect to keep in mind for a CNS emphasis day is low-grade plyometrics. The concept of absorbing force, accepting body weight, and re-directing force during all athletic movements is discussed in great detail throughout Bommarito University (example, see Coaching Videos section with Foot/Ankle Preparation). This can be at extreme joint loading levels on maximal sprints, like seen on exercises like Resisted Linear Sprints, Pulley Assisted Over-speed Sprints, and Pulley Assisted Over-speed to Cut-Up Drill. It can also be expressed with extreme joint loads from a deceleration to re-acceleration phase – as seen for exercises like DB Backpedal to Forward Cuts, WR Cut-Up Drill, and all Acceleration-Deceleration Zones. With all Change Of Direction (COD) drills, the limb speed is great, as well as extreme joint loads. Setting the foundation for absorbing force, accepting body weight, and re-directing force can also be expressed WITHOUT extreme joint loading, which is the concept behind Agility ladder drills. These can be considered low-grade plyometric exercises that SETS THE BASE for advanced joint loading. These drills are performed as basic reflexive mechanisms, with utilization of both of the edges of the feet, and basic acceleration off of these edge-drills.
Another concept that can be extremely effective during the Monday CNS day is Power Endurance and Eccentric Loading drills. This is where drills such as the Slideboard series can be very effective. On the standard Slideboard drill of Lateral Slides, the eccentric loading into the basic stretch reflex into the lateral push can set the base for higher speed COD later in the week. The linear and lateral lunge series does a great job of loading the adductors and hip flexors in extreme joint angled positions. This type of eccentric work is valuable for really high-speed COD exercises later in the week where getting into low positions with extreme joint angles is a constant.
Sport-Specificity
Note the main difference on the Training Script between the offensive and defensive skill positions is the application of the footwork drills. After a good round of overall footwork in the Agility Ladder, there is an application portion – technically a “burst sprint” out of the last ladder rung into a designated distance (typically 4-8 yards). The defensive skill players still need to work on hip mobility and pivots, so they will plant the first step out of the ladder, pivot and turn and sprint. The offensive skill players just need to maximize their first step acceleration in a linear fashion or a multi-directional fashion (angled first step off the edge of the foot into a linear sprint). This same type of system can be utilized with MicroHurdle agility, quick foot Rapid Response drills, or basic 2-step cone cutting drills.
Linemen typically do more linear training on Monday’s. This is because they typically have Tuesday’s off running to limit the overall pounding. Plus, the linear speed they train in is usually a much shorter distance, so they don’t need the Monday to prep the CNS for an efficient linear day on Tuesday (as compared to the skill position players). If they do any footwork drills, it is typically put into the CAMPS section in a much lower volume as part of the circuit.
TUESDAY – LINEAR SPEED DAY
- High Neural loads
- High Joint Loads
- CAMPS
- Absorption Force, Accepting body weight, Re-directing force – high volume/intensity
- Continuous metabolic energy system development style of muscle prep, joint isolation, and overall mobility/stability
- Overall Training Volume – high
No matter what is constantly being argued in the profession about the necessity of linear speed training for football players, IT IS ABSOLUTEY ESSENTIAL TO OVERALL DEVELOPMENT OF FOOTBALL PLAYERS. Remember we are Performance Coaches, NOT football coaches. We are developing the CNS, developing the muscles and all of the muscle properties, developing energy systems, and developing joint integrity to withstand all of the forces across joints that will be seen in the sport/position. We are TRAINING MUSCLES, NOT RE-CREATING THE EXACT MOTIONS SEEN IN SPORT. The best way to get better at football is to play football. You can’t possibly “recreate football” in its exact sense during training. Even if you could, how much do you really want to continue to beat up the joints in the off-season by re-creating the exact same repetitive motions seen in football? As with anything related to Performance Training for any sport, the volume and intensity of each system needs to be intelligently periodized to maximize development and avoid overtraining. This includes volumes of loads places across the joints.
Think of it this way: if you run in a straight line full speed and get up to that 20+ MPH zone, there is extreme joint loads during all of the Ground Contact phases of each step. If you are moving full speed and then have to change directions, you are decelerating the weight of your body at that speed, adding in numerous additional joint forces across many joints, adding in muscle action of additional contributions of the Glenohumeral abductors and adductors, adding in additional challenges of stabilizing the foot/ankle, adding in rotational components of the femur, tibia, etc. – plus many more actions. While this is a necessary END-RESULT that should be trained, all of these sub-categories of what occurs during a change of direction can be trained and isolated individually to make the END RESULT of the actual full speed COD more efficient. Even if a drill that isolates one of these sub-categories doesn’t “look like the actual motion seen in sport”, doesn’t make it any less important to the success of this eventual END RESULT. Linear sprinting falls into MULTIPLE aspects of these “sub-categories” that will make a football-specific COD much more effective.
Here is one of MANY examples that relates linear sprinting to a football-specific COD: linear sprinting still has dynamic action of the hip during Recovery phase, a powerful stretch reflex during Transitional phase, dynamic hip extension during Ground Preparation phase, and lower-joint loading (but still effective!) during Ground Preparation phase, and high emphasis on limiting time in Residual Phase. The EXACT same phases of motion will occur on any stride coming out of a COD. Hence, training for linear acceleration will enhance each phase of motion that occurs when the limb is not in contact with the ground – developing more muscle action during these phases. This enhanced muscle action will make the phases more efficient on the step OUT OF the COD (and each succeeding step) – hence, making the overall COD a lot more effective.
Note in the Training Script that there are a lot of circuits built into the application side of this day. There is a heavy emphasis on Resisted work. Again, resisted work is not as sport specific as the actual sport of football (or free runs) because there is a longer ground contact. However, dynamic action of resisted hip/knee extension combined with the stretch-reflex in the foot/ankle joints while driving through this resistance is extremely effective at raising the threshold of stored elastic energy. This increased threshold will transfer to a more dynamic, free (non-resisted) run. Note there is a constant complex between varying modes of free work with resisted work. In a sense, we are raising the threshold, and then applying it. Then going back and raising the threshold, and applying it again. Then, repeating again. The key is the PROGRESSIVE VOLUME AND INTENSITY of the threshold-raising (resisted) systems versus the application (non-resisted) systems on a week to week basis; and periodized around weight room work so there is minimal interference.
Sport-Specificity
Note that the Linemen are off on this Linear Speed Day. Typically Lineman really only need 3 days of active movement. And they usually benefit more to going every other day (note the Monday, Wednesday, Friday). The 4thday is primary upper body energy system development, usually set on Thursday. Because the linear speed training for lineman is usually much lower volume and much shorter distances, the neural input for this style of linear training is much lower. Hence, there is some of this linear training on Monday, with a low volume of linear on the other days (Wednesday – Position work; and Friday – Metabolic conditioning)
With regards to the skill players, note that the basic script for all positions that are not lineman are very similar with regards to linear speed. This is an aggressive script that can really maximize speed, power, first step acceleration, drive phase, transition, etc. There isn’t really too much specificity that can be between offensive and defensive skill players.
When getting in the “tweener” type players (like bigger, blocking Tight Ends; bigger, run-stopping middle linebackers; bigger LB that function a lot as DE in some situations) – it’s not necessary to have a separate script. It’s usually simplistic enough to just combine the scripts.
WEDNESDAY – UNLOADED RECOVERY
- Low Neural loads
- Low Joint loads
- CAMPS (CNS Activation and Muscle/Joint Preparation Systems)
- Low and unloaded
- Overall Training Volume – low
The great thing about being in the pool is that it will unload approximately 85% of the body weight. This allows for a lot of slow isometrics for overall joint mobility and stability in the CAMPS section.
The bounding and jumping plyometrics in this unloaded day is heavy volume. While vertical and horizontal plyometrics (long response and short response) is essential to peaking power, it really loads the joints when done on dry land. While this can be an effective training method, you really want to pick your battles in terms of volume with elite level football players. A good volume of vertical plyometrics can be appropriate in the weight room setting because of landing on a plyo box will lessen the impact of the land. On dry land, it can be much more appropriate to perform jumping and bounding plyometrics in the pool because the training effect will still be expressed without the excessive joint loads. Note in the Training Script that there is a plyometric circuit of vertical jumps complexed with horizontal split cycle jumps.
The movement circuit is mainly for power endurance. The power will be expressed because of the water resistance through the phases of the sprint cycle drills. And there is a good mix of loaded technical drills complexed with completely unloaded drills with no ground contact.
Sport Specificity
Note that the linemen typically will have success in performing their Position-Specific Day on Wednesday. Their “recovery day” will be a complete day off from all lower body field work on Tuesday. For the skill positions that hit field work on Monday, Tuesday, Thursday, and Friday, there can still be a good amount of work that gets performed on Wednesday – either a complete day off, or recovery work in the pool. One of the best aspects of regeneration is active regeneration – as demonstrated in this basic pool script.
The lineman specific day is usually best utilized as complex circuits. Note that the first circuit in the Training Script is a heavy strength endurance with standard Tire Flips, followed by a specific multidirectional movement in the Hoop Drills, followed by forearm endurance with the Farmer Walks.
Basic acceleration/deceleration zones in a linear fashion will be placed between the two circuits. The zones are short, but still play an important role in overall braking and deceleration forces. Even though it’s non-specific and linear, the overall muscle preparation of eccentric loading is tremendous. This muscle preparation will continue to enhance any specific multi-directional motion.
The final circuit is extremely advanced. The acceleration and deceleration zones are put into the specific Hoop Drills to greatly intensify the challenge of the deceleration and bending motions. The Back Sled Sprint is a strength endurance to continue to really focus on the knee extensors. No matter how strong the legs get through standard strength training, there is a tremendous benefit to transferring this strength to low bending positions when the knee extensors are overloaded. Even though this looks like a “Defensive Back” drill, there is definitely a transfer of “playing low” and “bending” in and out of a lineman stance – for both Offensive and Defensive Linemen. We’ve noticed more success in the succeeding rounds of the Acceleration/Deceleration Zone Hoop drills, even though the “fatigue” factor sets in. A lot of this success can be attributed to the Re-Directing of force and the increased threshold of the knee extensors seen in the complexing Back Sled Sprint drills. Trunk and Spine Power rounds out the second Linemen Circuit.
THURSDAY – POSITION-SPECIFIC DAY
- High Neural loads
- EXTREME Joint Loads
- CAMPS
- Absorption Force, Accepting body weight, Re-directing force – low volume/intensity
- Unloaded Speed – EXTREME volume/intensity
- Overall Training Volume – EXTREME
Note that the preparation for this session is extremely specific. Instead of performing a standard “warmup” or “stretch”, it can be much more appropriate to just prep the foot/ankle, and then spend a good period of activation, and simulation of movements. There is a full “Unloaded Speed Preparation” in the Coaching Video section of BPSU. This is the day that can utilize this entire script as a very appropriate preparation to the training day.
The Defensive skill players begin their day on the Training Script with the Back Lunge Series. This is the ultimate preparation system for all backwards motions. It really transfers well to BackPedal (BP) and AnglePedal-Weave (AP) motions because of the overload at absorbing and re-directing force at such extreme ankle dorsiflexed positions. The first BP/AP to change of direction (COD) circuit focuses on forward cuts. Because the Back Sled Sprint drill does such a good job of overloading the re-direction of force, it can be appropriately placed in this circuit as a complex. Remember that the forward cut motion relies heavily on the re-direction of force at extreme angles.
For defensive players, the acceleration/deceleration zones in a linear fashion will precede the final BP/AP COD Circuit, which focuses on Back Cuts – which utilizes more of a hip pivot than an extreme re-direction of force (as seen in the forward cuts). One interesting complex that is proven to be very effective is a few Assisted Over-speed Acceleration sprints that can conveniently precede the final circuit. Most defensive skill players (especially Defensive Backs) can benefit greatly from increasing stride length through this extreme horizontal plyometric-based exercise. There can be a tremendous transfer to the Back Cut series, because the sprint motion off of the hip pivot usually requires a full speed linear acceleration.
Note that the offensive skill players are setup very similar to the defensive systems. The same CAMPS system is used. The main difference happens upon the continued preparation. Note in the Training Script, offensive players now focuses on stabilizing the trunk/spine through rotation with the Single Arm Sled Marches. This is followed by absolute speed technical mechanics, and some general free acceleration sprints. Then, the first specificity circuit begins with heavy joint loading with inside-edge and outside edge change-of-direction (COD) drills with the Pattern Tree Cut-Up drill. A basic form is the single cut; with advanced challenges in the double cut. The same Acceleration/Deceleration zones as the defensive skill players are performed next. With the same concept – overload the braking and deceleration forces and intensify the re-direction of force into the re-acceleration. Putting a basic acceleration/deceleration zone on the front of it then intensifies the Cut-up drill series. The speed into the first cut will be at an extreme speed, which overloads the challenge of the edge cut. Note that the same Pulley Assisted Over-speed can be placed towards the end. Offensive players really benefit from performing a basic Cut-up off of the end of the assisted acceleration run.
One important point is that for any skill player performing an Assisted Over-speed run, there must be a great deal of preparation and limiting asymmetries in any joint. Not every player gets to this phase, even after a solid foundation is prepared in the 3 preceding macrocycles. If an athlete is ready, ensure that the day begins with stabilization of the trunk (most commonly used with success is the Single Arm Sled March). Because this advanced system of training is more commonly beneficial to offensive players, the day begins with this stabilization exercise sequence.
The Lineman on this day completely unloads their legs. This continues with the concept of running every other day. Since the heavy position day was Wednesday, the specific of linemen can now focus on the upper body. Remember that linemen are combat athletes. The endurance and power endurance of the upper body is one of the most underrated and under-utilized systems in their entire overall development of all combat athletes. The battle ropes is pure power endurance and grip endurance. The Tunch Punch will focus on hand speed, punching technique and power, and power endurance. The Landmine Jammer is resisted punching endurance and power endurance. And the Band Jammer is setup as the most specific in terms of the actual punching motion. The Band Jammer is also efficient at peaking power because of the accommodating resistance of the band.
FRIDAY – METABOLIC CONDITIONING
- Low Neural loads
- Medium Joint Loads
- CAMPS
- Absorption Force, Accepting body weight, Re-directing force – low volume/intensity
- Very specific and targeted muscle preparation, joint isolation, and overall mobility/stability
- Overall Training Volume – medium to high
There are varying forms of Energy System Development (ESD) that can be appropriate for football players from a metabolic standpoint. These are some efficient examples that can be used over the course of an off-season:
- Standard quantified and progressive interval training
- Varied quantified and progressive interval training
- Localized Strength Endurance
- Unloaded machine-based interval training or aerobic base development
The Training Script focuses on Localized Strength Endurance. This is an extremely underrated form of overall development for football players. From a football standpoint, it is not that difficult to develop and maximize the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Basic interval training the focuses on Power and Power Endurance in a fatigued state is important, but doesn’t’ need to be as much of an emphasis as many programs show. Further, much of this specific interval work is developed in the other days; even though there are speed and position drills. The work:rest ratio on Monday, Tuesday, and Thursday dictates the varying energy systems to be developed; so it doesn’t necessarily always have to be replicated on the Conditioning Friday.
Think about it from this example: the Hip Extensors can get strong and powerful in the weight room, but what about repeated bouts of strength? Local muscular fatigue is very common in football; much more then simply “being out of breath.” For the strength to transfer efficiently, utilizing strength endurance exercises like basic Sled March forward can be very appropriate. When executing the Sled March, the foot is placed in from the of the center of mass, with the heel striking first, then the emphasis of moving the sled forward is placed on concentric hip extension. This repeated bout of controlled marching for specified distances is a great example of specific, localized Strength Endurance. Note in the Script that there is a progressive increasing load of increased distances.
For skill position players, there still is a good technical phase after CAMPS that is focused on acceleration and absolute speed. The linemen are more focused on resisted acceleration work in extreme joint positions (see the low sled push work). The linemen didn’t have a full day focused completely on linear speed like the skill players, so they finish up their volume of linear speed work before the conditioning starts. The skill players need more overall sprint volume in the week, so the high volume of technical drills works well on the Conditioning Friday.
PROGRESSIVE OVERLOAD
This Training Script is based around one sample week of an entire macrocycle. Many examples are shown here about how to rotate from week to week. As with any intelligent weight room program, the volume and intensity and choices of exercises with speed and movement needs to be planned and periodized carefully. The theme of each day will remain constant. However the overall volume of the following aspects needs to be considered when building the overall macrocycle:
- Unloaded-joint training versus Loaded-joint volume
- Technical versus Application drills
- Time on each aspect of CAMPS
- Resisted versus Free (non-resisted) work
- Assisted versus Free (non-assisted) work
- Joint Preparation and Stabilization and minimizing assymetries versus Assisted work
- Weekly and overall volume of specific and/or multidirectional work
- Rotating the metabolic ESD emphasis weekly
- Volume of the various forms of ESD, and rotating the work:rest ratios – on EACH day, not just the Conditioning Friday
- Minimizing interference with weight room development
- Volume of Power to Power endurance work
- Volume of Strength to Strength endurance work
- Unplanned periodization changes based on readiness to train
This basic Training Script is a great start to a method for all elite and professional football players. It has been shown to be extremely effective at the elite high school, collegiate, and professional levels. However, as with any program – it’s the overall manipulation of the variables that is directly related to the success.
Pitchers and Quarterbacks
Pitchers and quarterbacks require unique types of training systems to increase throwing velocity and endurance. At BPS, we use a 5-point system to develop these “throwing athletes.” The 5-points are MB (med ball) RNT (reactive neuromuscular training), MB power, balance and deceleration, strength endurance, and power endurance.
5-POINT SYSTEM:
#1 MB RNT
#2 MB POWER
#3 POWER ENDURANCE
#4 STRENGTH ENUDRANCE
#5 BALANCE AND DECLERATION
This week we are focusing on med ball RNT, specifically “MB shoulder RNT.” This exercise shown in the video challenges the trunk rotator muscles, which are heavily utilized by pitchers and quarterbacks when they throw a ball. This exercise causes the athlete to accelerate the ball towards the wall. Then, after the ball bounces off the wall, the athlete is required to decelerate the ball. This is an important ingredient in the recipe to develop a powerful stretch reflex of the trunk rotators. With an appropriate volume and specific intention of using the trunk rotators the athlete will increase power output. Also, every other MB RNT exercise we have in the ‘#1 MB RNT’ list is in this video for all to reference. Each exercise has many linear, lateral, etc variations. The video shows one variation for each exercise. The video plays the exercises in order just as they are listed.